What is Laminated Veneer Lumber?
Laminated veneer lumber, commonly abbreviated as LVL, is an engineered wood product. It is made by bonding thin wood veneers together with adhesives...
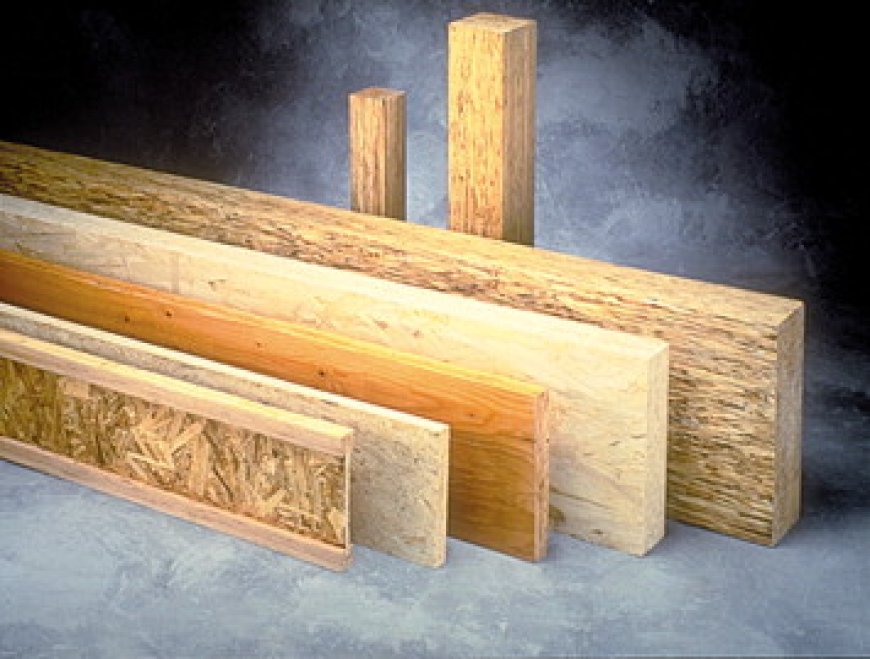

Laminated veneer lumber, commonly abbreviated as LVL, is an engineered wood product. It is made by bonding thin wood veneers together with adhesives. The veneers are oriented in the same direction to increase strength.
LVL offers several advantages over traditional lumber. It is less likely to warp, twist, or shrink. This makes it ideal for structural applications such as beams and headers. Additionally, it can be manufactured in longer lengths, allowing for greater flexibility in construction projects.
Definition and Composition
LVL consists of multiple layers of thin wood veneers. They are bonded together using strong adhesives. The grain of each veneer runs in the same direction, optimizing strength and stability.
The manufacturing process involves rotary peeling of logs. The veneers are dried, layered, and pressed together under heat. This results in a strong and durable product. Lumber Estimating Services often incorporate LVL due to its predictable performance, which helps in precise project planning and budgeting.
Manufacturing Process
The first step involves peeling logs into thin veneers using a rotary lathe. The veneers are then dried to reduce moisture content, ensuring better adhesive bonding. After drying, the veneers are clipped to remove defects and achieve uniform thickness.
Next, the veneers are coated with strong adhesives and laid up in the same direction. The layup is then pressed under heat to bond the veneers together, creating a stable and robust product. This process enhances the structural integrity of the material and ensures consistent performance in various applications.
Structural Properties
Understanding the structural properties of LVL is crucial for its application. It boasts high strength and stiffness due to the alignment of wood grains. This makes it suitable for heavy loads and long spans. Its consistent quality and performance also enhance reliability in construction.
Additionally, LVL resists bending and warping, providing stable structural support over time. Its uniformity minimizes the variability typically found in traditional wood. Thus, it offers predictable and dependable results for builders and engineers.
Applications in Construction
LVL is commonly used in many construction settings due to its strength and versatility. It serves as beams, joists, and headers in both residential and commercial buildings. Its ability to support heavy loads and long spans makes it ideal for these applications.
Moreover, LVL is valued in prefabricated and modular construction. It can be manufactured in large sizes, reducing the need for joints and ensuring structural integrity. Its predictable performance allows architects and builders to design robust and reliable structures, which is essential for safety and efficiency in construction projects.
Advantages Over Traditional Lumber
LVL offers several benefits compared to traditional lumber. It is engineered to be consistent in quality, reducing the variability found in natural wood. This uniformity ensures reliable structural performance in construction applications.
Moreover, LVL resists common issues such as warping, twisting, and shrinking. This stability makes it a preferred choice for builders who need predictability in their materials. Additionally, its ability to be manufactured in longer lengths reduces the need for joints, simplifying construction and enhancing structural integrity.
Environmental Impact
The manufacturing process of LVL uses less wood than traditional lumber. This efficiency reduces the number of trees needed for construction projects. By utilizing nearly the entire log, waste is minimized, and more sustainable practices are achieved.
Additionally, the adhesives used in LVL production are eco-friendly. They emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to better air quality. LVL's durability means structures last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements. All these factors make LVL a more environmentally responsible choice in the construction industry.
Cost Considerations
LVL can be cost-effective due to its efficient use of materials. It utilizes thin wood veneers bonded together, which optimizes the use of raw materials and minimizes waste. This efficiency reduces the number of trees required, lowering the overall cost of production. Additionally, LVL can be manufactured in longer lengths, reducing the need for joints and speeding up the construction process.
Labor costs are often lower when using LVL. The predictable quality and performance of LVL simplify planning and reduce the potential for errors. This reliability leads to fewer delays and cost overruns, making it a financially sound option in construction projects.
Safety and Durability
Safety and durability are key advantages of using LVL in construction. Its engineered nature provides consistent strength, reducing the risk of structural failures. This reliability ensures that buildings meet safety standards efficiently.
LVL's resistance to warping and twisting means it maintains integrity over time. This stability minimizes repair and maintenance costs, making it a durable choice. With fewer defects and a uniform structure, it stands up well to heavy loads and harsh conditions. Thus, it provides a long-lasting, safe solution for various building needs.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Industry standards ensure that LVL used in construction meets specific quality and safety benchmarks. These standards deal with the manufacturing processes, material properties, and performance criteria. This helps ensure consistency across different producers and products.
Regulations govern the use of LVL in various construction applications. They set requirements for load-bearing capacities, dimensions, and installation practices. Compliance with these regulations ensures that structures are safe and reliable. Adhering to established guidelines is vital for builders and engineers to meet both legal and safety obligations.
Conclusion
In summary, LVL proves to be an advantageous material in the construction industry. Its engineered design provides uniform strength and stability. These qualities make it reliable and consistent, which is critical for safe building practices.
Additionally, it offers environmental benefits due to efficient material use and lower emissions from adhesives. The cost-effectiveness and reduced labor efforts contribute to its popularity. By reducing maintenance needs and enhancing structural integrity, it provides a long-lasting solution. Thus, it serves as a sustainable and practical choice for builders and engineers.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0