Cutting the Cord: How Wireless Power is Revolutionizing the Way We Charge
The global wireless power transmission market is expected to reach USD 186.76 billion in 2030, with a CAGR of 20.39% during the forecast period 2023-2030
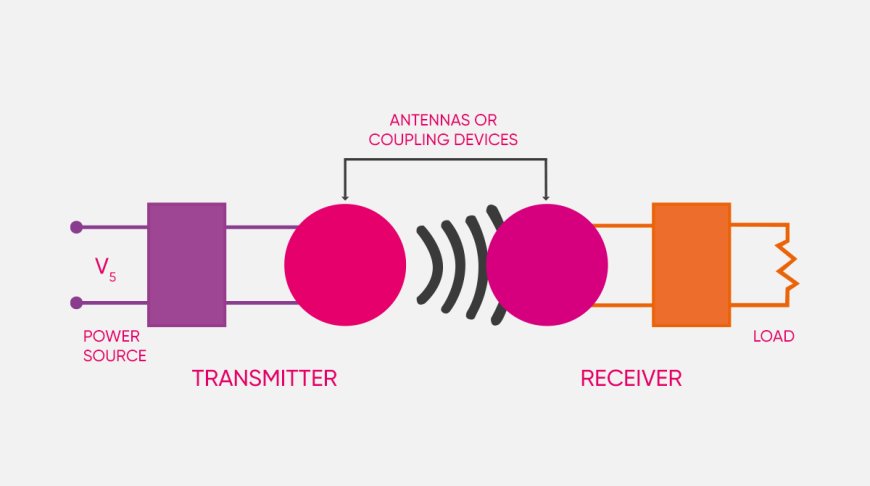
The Infinium Global Research analyzes the Wireless Power Transmission Market over the period of 2024 to 2032. This report also provides detailed qualitative and quantitative analyses of the market dynamics, market size and future trends in global wireless power transmission market. It will help a lot of decision makers to develop strategies and find new opportunities in the global markets of wireless power transmission. The report covers market changing aspects including drivers, restraints, opportunities, and trends expected to encouragement the expansion of the wireless power transmission market during the period.
The global wireless power transmission market is expected to reach USD 186.76 billion in 2030, with a CAGR of 20.39% during the forecast period 2023-2030.
Get Sample pages of Report: https://www.infiniumglobalresearch.com/form/669?name=Sample
Market Dynamics
1. Demand Drivers:
People are ditching wired connections in favor of wireless because it's simpler and more convenient. We want strong wireless everywhere for our phones, laptops, music players, cameras, and more. Wireless lets us move around freely, connect quickly, and use our devices easily. This is why wireless charging is becoming so popular in smartphones, tablets, and wearables. As consumers keep demanding "go-wireless" options, the market for wireless power transmission is booming. Companies are making user-friendly, affordable wireless charging devices that last for years, which is driving up demand even more.
2. Opportunity
Wireless power isn't just for phones anymore! Researchers are using this technology to develop mini and micro robots that can be juiced up without wires. There's even a buzz around wireless-powered drones. The idea is for a transmitter to send high-frequency power to a receiver coil built into the robots or drones. Imperial College of London has already shown a drone that can fly above a wireless power transmitter just a few inches wide. In the US, ZiiEnergy is developing a drone receiver that follows Open Dots Alliance standards and can zap drones with a whopping 45 watts of power.
3. Challenge
Wireless charging is booming in consumer electronics, making life easier for smartphone, tablet, and smartwatch users. But there are still some hurdles to overcome. The charging range for these devices, which rely on electromagnetic induction or magnetic resonance, is limited. This short range is a big headache for manufacturers, as the farther apart the transmitter and receiver are, the less efficient the power transfer becomes. Safety is another major concern. Strong electromagnetic fields can potentially harm living things, which is a big red flag. This is why so many startups jump into this market, full of ideas and prototypes, only to fizzle out before launch. The challenges of safety and efficiency are tough nuts to crack, and they're keeping some promising products from seeing the light of day.
Regional Analysis
The world market for wireless power transmission is divided into four main regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa. Right now, North America is the leader, in part because manufacturing is booming in Mexico thanks to lower costs. This feeds the high demand for wireless charging in countries like the US and Canada. But that's expected to change. The Asia Pacific region is projected to take the lead soon and drive future market growth. This is especially true in countries like China and India, where the car industry is taking off. That means a big jump in demand for wireless charging in vehicles in the coming years.
Market Segmentation
· By Range: This looks at how far the power can be transmitted wirelessly. There are two main categories: near field and far field. Near field is for short distances, like charging your phone on a pad. Far field is for longer distances, and it's still under development for things like powering drones.
· By Technology: This refers to the specific method used to transmit power wirelessly. There are a couple of main options: inductive coupling and resonance (both near field), and microwave power transmission (far field). Inductive charging is what you see in most wireless charging pads today.
· By End User Industries: This looks at the different industries that are using or developing wireless power transmission technology. Consumer electronics (phones, tablets) are a big driver right now, but other industries like healthcare, automotive, and manufacturing are also exploring its potential for applications like powering medical devices, electric vehicles, and industrial robots. There's even some research into using it for things like drones and solar power satellites!
Competitive Landscape
Koninklijke Philips N.V., PowerbyProxi (acquired by Apple Inc.), SAMSUNG, Texas Instruments Incorporated, Integrated Device Technology, Inc. (acquired by Renesas), TDK CORPORATION, Powermat, WiTricity Corporation, PLUGLESS POWER INC., and Salcomp Plc.
Report Overview: https://www.infiniumglobalresearch.com/market-reports/global-wireless-power-transmission-market
Reasons to Buy this Report:
=> Comprehensive analysis of global as well as regional markets of wireless power transmission.
=> Complete coverage of all the product types and application segments to analyze the trends, developments, and forecast of market size up to 2032.
=> Comprehensive analysis of the companies operating in this market. The company profile includes an analysis of the product portfolio, revenue, SWOT analysis, and the latest developments of the company.
=> Infinium Global Research- Growth Matrix presents an analysis of the product segments and geographies that market players should focus on to invest, consolidate, expand, and/or diversify.
Conclusion:
Wireless power transmission (WPT) uses electric, magnetic or electromagnetic fields to juice up devices without wires. This tech is especially useful for things that move around a lot, like robots and phones. The market for WPT is growing because more and more devices are battery-powered and need efficient charging. New applications like solar-powered satellites beaming energy down to Earth are also on the horizon. Improvements in efficiency and the growing popularity of wireless charging in smartphones and electric vehicles are fueling this market. However, challenges like interference with communication systems and the high cost of the technology are holding it back. Even the recent pandemic slowed things down by disrupting production and creating raw material shortages. But overall, the future looks bright for wireless power transmission.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0












































