How Urticaria Specialists Diagnose Hard-to-Treat Skin Reactions
This blog will guide you through how urticaria specialists evaluate complex hives, what diagnostic steps they take, and how their approach differs from general dermatology or primary care.
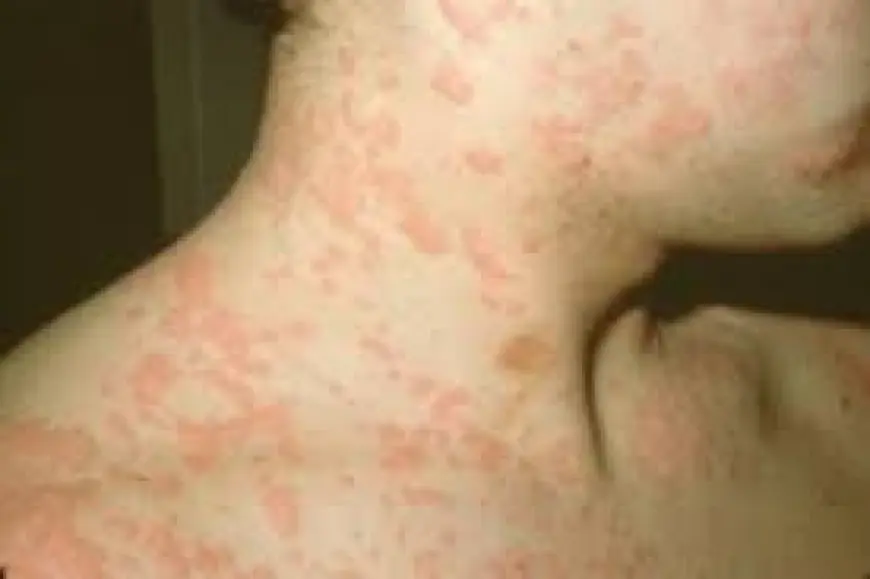
Chronic skin reactions like persistent hives can be incredibly frustrating. When itching, swelling, and redness return again and again—despite over-the-counter medications—it’s time to ask: what’s really causing this? That’s when the expertise of urticaria specialists becomes essential.
Why Standard Diagnosis Often Falls Short
Most people who develop hives initially visit a general physician or allergist. In many cases, acute urticaria resolves within days or weeks with simple antihistamines. But for individuals with recurring or long-lasting hives, the cause is often more complex.
These patients may face:
-
Weeks of trial-and-error medications
-
Incomplete allergy testing
-
Misdiagnoses like eczema or stress rashes
-
No clear explanation for what triggers their outbreaks
That’s when urticaria specialists are uniquely positioned to go deeper and uncover hidden patterns or root causes.
What Makes Urticaria Difficult to Diagnose
Urticaria is a condition with many possible types and triggers, including:
-
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (no known cause)
-
Inducible urticaria (triggered by physical factors like cold, pressure, or heat)
-
Autoimmune-related urticaria
-
Urticaria caused by underlying systemic disease
Most cases of chronic urticaria have no clearly identifiable allergen. This is why traditional allergy tests often return normal results, leaving patients frustrated.
Urticaria specialists are trained to distinguish between these variants and investigate beyond the surface.
What to Expect During a Diagnostic Evaluation
1. Detailed History Taking
One of the most important tools urticaria specialists use is a comprehensive medical history. This includes:
-
Duration and frequency of hives
-
Triggers like stress, pressure, or temperature
-
Response to medications
-
Family or personal history of autoimmune disease
-
Associated symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, or fevers
-
Previous diagnostic tests and treatments
This background helps the specialist understand whether the urticaria is likely autoimmune, physical, allergic, or idiopathic.
2. Physical Exam
The visual presentation of hives can offer key diagnostic clues. During the exam, urticaria specialists may:
-
Observe hive patterns (e.g., shape, location, time of appearance)
-
Apply controlled physical stimuli (cold, heat, vibration) to provoke a response
-
Check for signs of angioedema or other systemic inflammation
This hands-on approach allows for identification of rare types of urticaria that may be missed in standard exams.
3. Targeted Testing
Unlike routine blood panels, urticaria specialists order specific tests based on suspected causes. These may include:
-
Complete blood count (CBC) to check for signs of infection or inflammation
-
Thyroid function tests (TSH, T3, T4)
-
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and other autoimmune panels
-
ESR and CRP to measure inflammation
-
Serum tryptase or histamine levels
-
Skin prick testing or serum IgE (only if allergy is suspected)
In some cases, challenge testing is used to confirm inducible urticaria by exposing skin to controlled stimuli (ice, pressure, etc.).
Why the Diagnosis Matters
Correctly identifying the subtype of urticaria is critical for effective treatment. For example:
-
Chronic spontaneous urticaria may respond best to biologics like omalizumab
-
Physical urticaria requires lifestyle changes to avoid specific stimuli
-
Autoimmune urticaria may need immunosuppressive therapies
-
Allergic urticaria must be managed by removing the allergen and using antihistamines
Only urticaria specialists have the tools and training to make these distinctions and build a personalized plan.
How Urticaria Specialists Build a Treatment Plan
Once a diagnosis is made, urticaria specialists create a multi-layered strategy:
Step 1: Maximize Antihistamines
Instead of standard dosing, they often prescribe higher or split doses of second-generation (non-drowsy) antihistamines.
Step 2: Add-on Medications
If symptoms persist, they may add:
-
H2 blockers like famotidine
-
Leukotriene receptor antagonists (e.g., montelukast)
-
Short-term oral corticosteroids (for flares only)
Step 3: Advanced Therapies
For severe or resistant cases, urticaria specialists may recommend:
-
Omalizumab (a biologic injection)
-
Cyclosporine or methotrexate (in autoimmune urticaria)
-
Dietary adjustments for histamine sensitivity
They may also refer to rheumatologists or endocrinologists if urticaria appears to be linked to a broader systemic condition.
Emotional Support and Education
Beyond diagnosis and medication, urticaria specialists understand the psychological toll of living with chronic skin flare-ups. Many patients experience:
-
Anxiety from unpredictable hives
-
Embarrassment in public settings
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Depression due to the chronic nature of the condition
Specialists often incorporate mental health support, lifestyle counseling, and long-term follow-ups to improve the patient’s overall well-being—not just the skin symptoms.
Conclusion
Chronic urticaria may seem like a skin-deep issue, but its root causes can be complex, multifactorial, and difficult to manage without proper guidance. When over-the-counter remedies and general physicians can no longer help, it’s time to consult urticaria specialists.
With advanced testing, in-depth knowledge, and access to innovative treatments, urticaria specialists offer a clear path forward for those struggling with hard-to-treat hives. If your skin isn’t getting better—or you’re tired of managing symptoms without answers—it may be time to take that next step.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0