Trusted Neurology Care for Trigeminal Neuralgia & Nerve Pain
Trigeminal neuralgia is one of the most painful neurological conditions known, often described as sudden, sharp, electric shock-like pain that affects one side of the face.
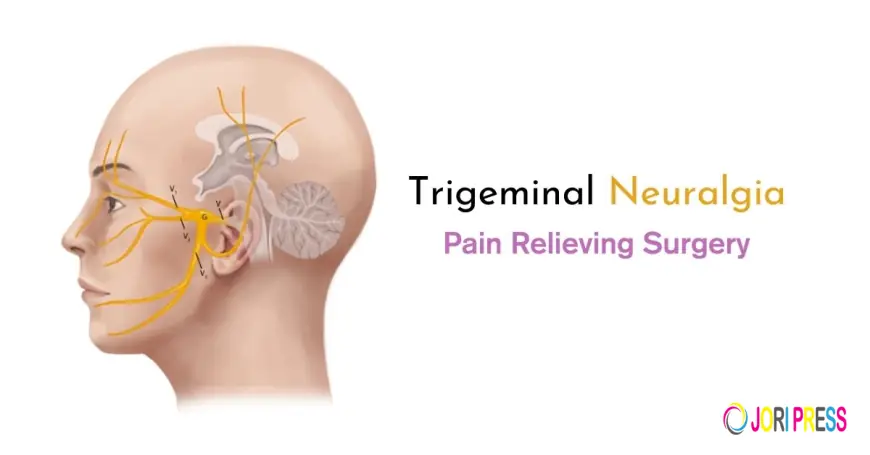
Trigeminal neuralgia is one of the most painful neurological conditions known, often described as sudden, sharp, electric shock-like pain that affects one side of the face. This condition arises from irritation or compression of the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for facial sensations. Even simple actions such as brushing teeth, eating, or speaking can trigger excruciating pain episodes. At the Neurology and Pain Management Clinic (NPMC), Dr. Gautam Arora (MBBS, MD, DM) offers expert and compassionate care for patients struggling with trigeminal neuralgia and other forms of nerve pain, using the latest diagnostic and treatment techniques for effective relief.
Understanding Trigeminal Neuralgia and Nerve Pain
Trigeminal neuralgia occurs when the trigeminal nerve, which divides into three branches controlling the forehead, cheek, and jaw, becomes compressed or irritated. The compression is often caused by a blood vessel pressing against the nerve near its connection to the brainstem. In some cases, multiple sclerosis, facial injury, or nerve damage may also be contributing factors.
Patients typically experience intense, stabbing pain that lasts from a few seconds to minutes, often recurring several times a day. Over time, this pain can become chronic and emotionally distressing, affecting eating, sleeping, and social interactions.
At NPMC, Dr. Gautam Arora focuses on identifying the underlying cause of nerve pain to tailor treatment plans that provide lasting relief rather than temporary solutions.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
A precise diagnosis is essential to rule out other causes of facial pain, such as dental issues, sinus infections, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Dr. Gautam Arora conducts a detailed neurological examination and may recommend advanced imaging studies like MRI scans to detect nerve compression or structural abnormalities. In some cases, diagnostic nerve blocks are used to pinpoint the affected nerve branch.
Effective Treatment Options at NPMC
1. Medications:
Initial treatment often involves anticonvulsant medications such as carbamazepine or gabapentin, which help reduce abnormal nerve activity. Muscle relaxants and pain-modulating drugs may also be used depending on the severity of symptoms.
2. Nerve Blocks:
A trigeminal nerve block is a minimally invasive procedure where an anaesthetic or anti-inflammatory medication is injected near the affected nerve to provide immediate pain relief. These blocks not only ease discomfort but also help in confirming the diagnosis.
3. Radiofrequency Ablation and Neuromodulation:
For chronic or medication-resistant cases, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) offers long-term relief by disrupting the pain signals transmitted by the nerve. Alternatively, neuromodulation therapies, such as spinal cord or peripheral nerve stimulation, use electrical impulses to modulate pain pathways, significantly reducing discomfort.
4. Botox Injections:
In some patients, Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections can effectively reduce facial pain by relaxing affected muscles and decreasing nerve irritation.
Comprehensive, Compassionate Care
Living with trigeminal neuralgia can be overwhelming, but with expert care, it is manageable. At the Neurology and Pain Management Clinic (NPMC), Dr. Gautam Arora (MBBS, MD, DM) combines advanced treatments with a patient-centred approach to restore comfort and quality of life. Whether through medication, targeted nerve blocks, or minimally invasive procedures, patients receive personalised care designed for long-lasting relief.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0