Sustainability in the Pharmaceutical Industry and Cold Chain Optimization
This article explores sustainability in the pharmaceutical industry and examines real-world strategies that work such as green chemistry, waste reduction, renewable energy, ethical sourcing, circular packaging, and supply chain transparency. Practical guidance to make pharma more sustainable.
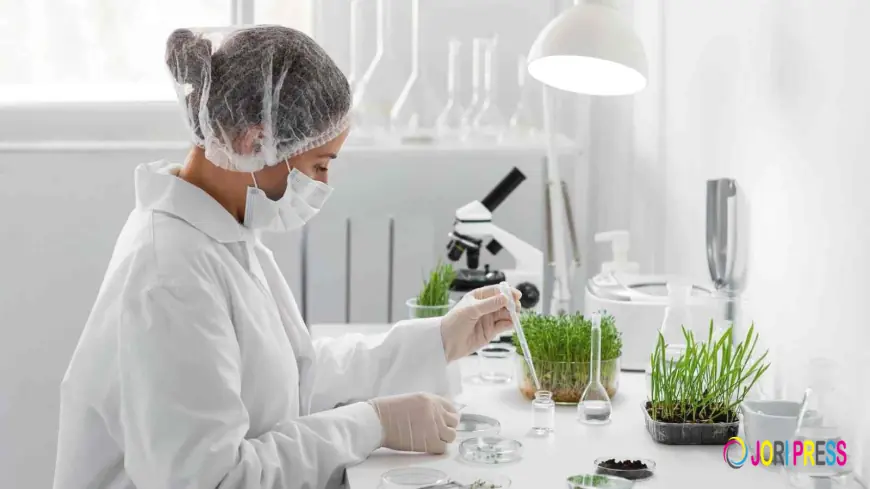

Environmental pressures regulatory demands and growing patient and investor expectations are pushing pharmaceutical companies to embed sustainability in their operations. Sustainability in the pharmaceutical industry is no longer a niche goal but a core part of competitive strategy. In this article we explore what sustainability means in pharma practice real-world strategies that work and how companies can move from aspiration to impact.
What Sustainability Means in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Sustainability in the pharmaceutical industry involves managing environmental impact across drug discovery manufacturing packaging distribution and disposal as well as addressing social responsibility and economic viability. It includes reducing carbon emissions water use and waste materials ensuring safe chemical usage and improving supply chain practices. True sustainability means balancing patient health outcomes with planetary health and resource preservation.
Major Drivers for Sustainability in Pharma
Regulatory requirements are tightening globally making emissions reporting energy usage and waste control mandatory in many regions. Investors and ESG frameworks increasingly reward companies with strong environmental performance. Patients and healthcare providers are more likely to trust brands that demonstrate ethical impact especially around safety waste and environmental footprint. Cost pressure also makes sustainability financially material with energy and resource efficiency leading to real savings.
Green Chemistry and Cleaner Manufacturing Processes
Green chemistry applies principles that reduce or eliminate hazardous substances optimize reaction efficiency and use renewable or safer raw materials. Cleaner manufacturing may shift from batch production to continuous manufacturing to reduce solvent use and lower energy demands. Adopting biocatalysts or alternative reaction pathways can cut waste in synthesis. Designing processes to reclaim solvents or reuse by-products enhances environmental performance and cost efficiency.
Reducing Energy and Water Footprint
Energy consumption in pharma manufacturing for heating cooling ventilation purification and chemical reactions is often high. Shifting to renewable energy sources investing in energy-efficient equipment and heat recovery systems can reduce carbon emissions significantly. Water usage can be reduced by closed loop systems water recycling waterless cleaning techniques and efficient cooling. Innovations in facility design and operational optimization further shrink footprints.
Waste Minimization and Circular Economy Practices
Waste arises from unused materials expired products packaging chemical byproducts and more. Minimizing waste means designing for reuse or recycling reclaiming raw materials and reducing overproduction. Circular economy practices include recovering solvents capturing and repurposing pharmaceutical by-products returning packaging components back into use and designing drug formulations to minimize leftover waste. Programs to collect unused or expired drugs also help reduce environmental load.
Sustainable Packaging and Logistics
Packaging contributes heavily to waste weight transportation cost and carbon emissions. Using recyclable biodegradable or lighter materials designing packaging that minimizes layers optimizing geometric shapes for shipping and reducing packaging volume reduce environmental impact. Logistics strategies such as route optimization cold chain efficiency consolidating shipments and using renewable fuel or electric vehicles help lower carbon emissions during transport.
Ethical Sourcing and Supplier Engagement
Raw material sourcing often drives large environmental and ethical risks including deforestation water pollution and poor labor practices. Working with suppliers who adhere to environmental and social standards performing audits and integrating sustainability criteria into procurement decisions improves supply chain risk resilience. Local sourcing when possible reduces transport emissions and improves supply chain transparency. Supplier collaboration on sustainability innovation amplifies impact.
Leveraging Digital Tools and Transparency
Digital monitoring systems IoT sensors real-time analytics track energy water use temperature in storage and logistics to flag inefficiencies. Blockchain or tracking platforms improve traceability of raw materials and waste streams enabling accountability. Lifecycle assessment tools help identify hotspots in the value chain. Transparent reporting to stakeholders investors and regulatory bodies builds trust and ensures continuous improvement.
Regulatory Compliance and ESG Reporting
Pharma companies must comply with environmental regulations around emissions water discharge chemical safety waste disposal and worker safety. ESG reporting frameworks require disclosure of sustainability metrics governance and social impact. Aligning internal strategy with standards such as ISO certifications science based targets or local environmental laws ensures legal compliance and may give access to incentives or grants. Clear metrics targets timelines and third-party validation strengthen credibility.
Conclusion
Sustainability in the pharmaceutical industry is both a moral imperative and a business opportunity. Strategies such as green chemistry energy and water reduction waste minimization circular economy practices ethical sourcing sustainable packaging digital transparency and regulatory alignment deliver measurable environmental gains financial savings reputational benefits and risk resilience. Companies ready to embed sustainability deeply across their operations stand to lead in innovation patient trust and long-term viability.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0