Allergy Testing 101: What You Need to Know Before Getting Tested
Allergies affect millions of people worldwide, causing symptoms ranging from mild irritation to life-threatening anaphylaxis. If you suspect you have allergies, getting an allergy test is the first step to identifying the triggers and managing your condition effectively.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know before getting tested, including the types of allergy tests available, how to prepare, what to expect, and how to interpret the results.
What Is Allergy Testing?
Allergy testing is a medical process used to identify substances that trigger allergic reactions in individuals. These allergens can be found in food, the environment, medications, or insect venom. Testing helps doctors diagnose allergies accurately and create a personalized treatment plan.
Why Should You Get an Allergy Test?
If you experience frequent allergic reactions such as sneezing, itching, rashes, difficulty breathing, or digestive issues, allergy testing can help you pinpoint the exact allergens causing these symptoms. Getting tested is crucial for:
- Managing seasonal allergies
- Identifying food allergies
- Diagnosing skin-related allergies
- Preventing severe allergic reactions
- Improving overall quality of life
Types of Allergy Tests
There are several types of allergy tests, and your doctor will recommend the most appropriate one based on your symptoms and medical history.
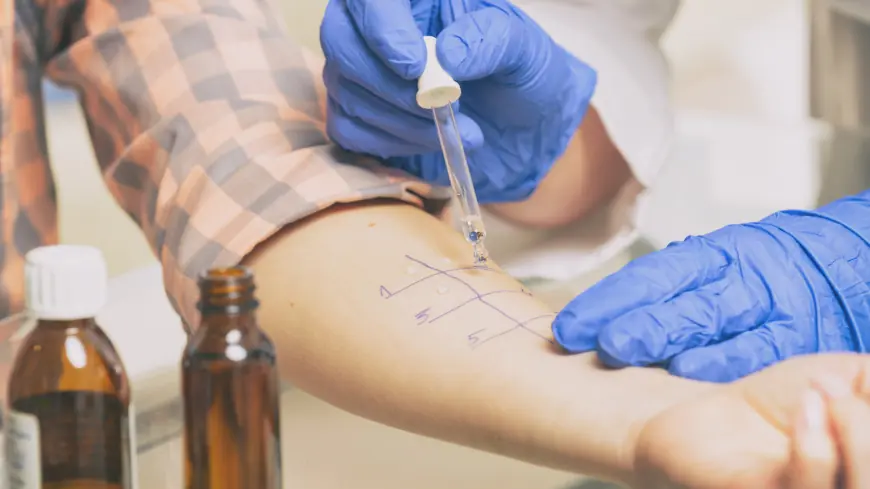
1. Skin Prick Test (SPT)
- How It Works: Small amounts of potential allergens are applied to your skin using a tiny needle or lancet. If you're allergic, a red, itchy bump will appear within 15-20 minutes.
- Pros: Quick, widely available, and relatively painless.
- Cons: Not suitable for people with severe skin conditions or those taking antihistamines.
2. Intradermal Skin Test
- How It Works: A small amount of allergen is injected just under the skin. This test is usually used when the skin prick test results are inconclusive.
- Pros: More sensitive than the skin prick test.
- Cons: Higher chance of false positives and a slightly higher risk of severe reactions.
3. Blood Test (Specific IgE Test)
- How It Works: A blood sample is drawn and analyzed for allergen-specific IgE antibodies.
- Pros: Ideal for individuals who can't undergo skin tests.
- Cons: Results take longer, and the test may not be as sensitive as skin tests.
4. Patch Test
- How It Works: Used to diagnose contact dermatitis by applying allergen-containing patches to the skin for 48 hours.
- Pros: Effective for identifying skin allergies.
- Cons: Time-consuming and requires multiple visits.
5. Oral Food Challenge
- How It Works: Under medical supervision, small amounts of a suspected allergen are consumed to monitor reactions.
- Pros: Considered the most accurate test for food allergies.
- Cons: Requires close medical supervision due to the risk of severe reactions.
How to Prepare for an Allergy Test
Before undergoing an allergy test, there are a few steps you should take to ensure accurate results:
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss your symptoms and medical history with an allergist to determine which test is best for you.
- Avoid Antihistamines: Medications like antihistamines can interfere with test results. Your doctor may ask you to stop taking them a few days before testing.
- Keep a Symptom Journal: Track when and where your symptoms occur to help identify potential triggers.
- Wear Comfortable Clothing: Some tests require access to your arms or back, so dress accordingly.
What to Expect During an Allergy Test
The procedure varies depending on the type of test you take. Generally:
- Skin tests are quick and may cause minor discomfort, such as itching or redness.
- Blood tests involve a standard blood draw and take a few days to produce results.
- Patch tests require you to keep allergens on your skin for a few days.
- Oral food challenges take longer and require close medical supervision.
Interpreting Your Allergy Test Results
After your test, your doctor will analyze the results and discuss your treatment options. Here’s what different results could mean:
- Positive Result: Indicates an allergy to a specific substance. You should avoid exposure and follow a treatment plan.
- Negative Result: Suggests no allergic reaction to tested allergens. Further tests may be required for an accurate diagnosis.
- False Positives/Negatives: Sometimes, tests can show misleading results. Your doctor may recommend additional tests if needed.
Next Steps After Allergy Testing
Once you know what you're allergic to, the following steps can help you manage your allergies effectively:
- Avoid Triggers: Reduce exposure to allergens in your daily life.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe antihistamines, nasal sprays, or epinephrine for severe allergies.
- Immunotherapy: Allergy shots or sublingual tablets may help desensitize you to allergens over time.
- Dietary Adjustments: If you have food allergies, work with a nutritionist to create a safe eating plan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is allergy testing painful?
Most allergy tests cause minimal discomfort, similar to a tiny pinch or mild itchiness.
2. How long does allergy testing take?
Skin tests typically take 20-30 minutes, while blood tests require a few days for results.
3. Can allergies develop later in life?
Yes, allergies can appear at any age, even if you’ve never had them before.
4. Is at-home allergy testing reliable?
At-home tests may not be as accurate as professional tests. It’s best to consult an allergist for definitive results.
Conclusion
Allergy testing is a crucial step in identifying and managing allergies effectively. Whether you suffer from seasonal allergies, food sensitivities, or skin reactions, proper testing can help you take control of your health. If you suspect you have allergies, consult with an allergist to determine the best testing method for you. By understanding your allergies, you can make informed lifestyle changes, reduce symptoms, and improve your overall well-being.

 izan
izan 










