Scale Inhibitors Market Growth: Share, Value, Size, Trends, and Insights
Introduction to the Scale Inhibitors Market
What Are Scale Inhibitors?
Scale inhibitors are chemical agents specifically designed to prevent the formation of scale—hard, crusty deposits of minerals like calcium carbonate or sulfate—inside pipes, equipment, and industrial systems. These minerals naturally occur in water and, when left untreated, crystallize to form deposits that can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy costs, and even complete equipment failure.
Scale inhibitors work by interfering with the crystal growth process. They either block the nucleation step (where particles begin forming crystals) or prevent crystals from sticking together and attaching to surfaces. Essentially, they act as a barrier between the equipment and the problematic minerals, making them invaluable in a variety of industries.
Their importance lies in their ability to save millions in maintenance and replacement costs. In systems like cooling towers, boilers, oil pipelines, and desalination plants, the use of scale inhibitors ensures smooth operation, fewer downtimes, and longer life cycles for the infrastructure.
Importance and Applications Across Industries
From the oil fields of the Middle East to municipal water systems in urban America, scale inhibitors are in high demand. Their versatility makes them essential in a wide range of industries:
-
Oil & Gas: To prevent scale buildup in wellbores and pipelines, especially in offshore rigs where mineral-heavy water is prevalent.
-
Power Generation: Boilers and cooling systems must remain scale-free to operate efficiently.
-
Water Treatment: Municipal and industrial water systems require constant scale control to maintain water quality and flow efficiency.
-
Food & Beverage: In industries where water purity is non-negotiable, like food processing and beverage manufacturing.
In each of these sectors, scale inhibitors help ensure not just operational efficiency but compliance with health and safety regulations. The use of environmentally friendly inhibitors is also becoming a growing trend, aligning with global sustainability efforts.
Market Overview and Growth Potential
Global Market Size and Forecast (2024–2030)
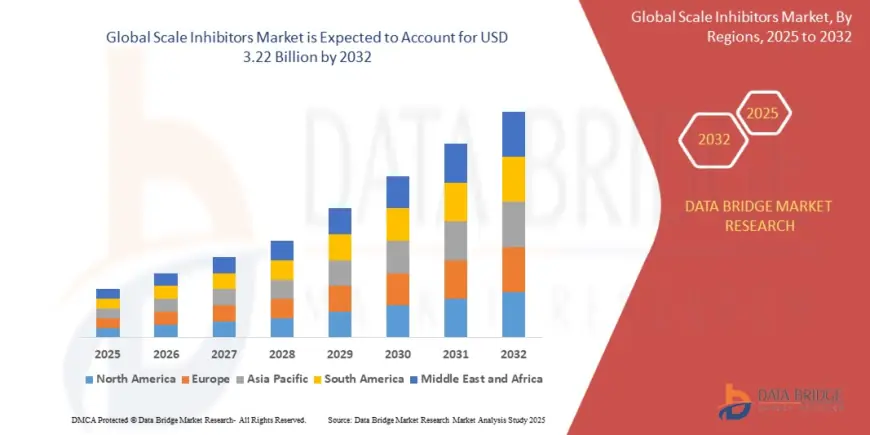
The global scale inhibitors market was valued at approximately USD 2.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 4.5 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of around 6.5%. This robust growth is fueled by increasing demand in end-use industries and advancements in chemical formulations that enhance inhibitor performance.
Rapid industrialization in developing nations and the expansion of oil and gas exploration are significant contributors to this market surge. Moreover, urban population growth is pushing municipal governments to improve water treatment infrastructure, creating a rising demand for water treatment chemicals.
APAC is currently the fastest-growing region, with countries like China and India ramping up industrial operations. Meanwhile, North America and Europe hold the lion's share in terms of technological development and usage, particularly in power generation and oil sectors.
Get More Links : https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-scale-inhibitors-market
Key Drivers Fueling Market Expansion
-
Industrial Growth: More factories and energy plants mean more potential for scale problems.
-
Aging Infrastructure: Older systems are more prone to scale buildup, needing more frequent inhibitor applications.
-
Regulatory Push: Governments mandating improved water treatment and energy efficiency are pushing industries to use chemical solutions.
-
Technological Advancements: Innovations like slow-release scale inhibitors or those combined with corrosion control are creating new opportunities.
Furthermore, the growing shift toward eco-friendly and biodegradable scale inhibitors is expanding the market’s appeal to environmentally conscious organizations.
Challenges Hindering Market Growth
Despite the booming demand, several factors pose a challenge:
-
Environmental Regulations: Some traditional inhibitors are not environmentally safe and face restrictions in developed countries.
-
High R&D Costs: Developing next-gen inhibitors that are both effective and eco-friendly involves significant investment.
-
Complex Supply Chains: Sourcing raw materials and ensuring consistent quality across global markets can be difficult.
-
Alternative Technologies: In some regions, industries are opting for physical or mechanical scale control methods over chemical inhibitors.
However, with the right regulatory strategies and innovation, these challenges can become stepping stones toward a more sustainable and profitable market.
Classification of Scale Inhibitors
Phosphonates
Phosphonates are among the most widely used scale inhibitors due to their excellent calcium tolerance and thermal stability. They are especially effective in high-pressure and high-temperature systems like oil wells and power plants. Their primary mechanism involves chelation and threshold inhibition, preventing the nucleation and growth of scale-forming minerals.
The only drawback? Environmental concerns. Phosphonates are not easily biodegradable, which has led to scrutiny in eco-conscious regions. However, their efficiency still makes them the go-to choice in applications where performance outweighs environmental constraints.
Carboxylates/Acrylic
Carboxylate or acrylic polymers are synthetic scale inhibitors known for their dispersing capabilities. They prevent small crystals from aggregating and forming large, damaging deposits. These inhibitors are particularly suitable for cooling towers and wastewater treatment plants where scale and suspended solids can wreak havoc.
They are also gaining popularity for being more biodegradable compared to phosphonates. However, they often need to be used in conjunction with other chemicals for maximum effectiveness.
Sulfonates
Sulfonate-based inhibitors are effective in high-hardness water systems, offering a reliable option for industrial settings with extreme conditions. They work well under a variety of pH levels, making them versatile. Their dispersing and sequestering abilities help maintain clean systems even in the most challenging environments.
While not as mainstream as phosphonates or acrylics, they’re slowly carving out a niche, especially in combination treatments where multiple inhibitors are used together.
Natural Polymers and Others
Natural polymer-based scale inhibitors are on the rise, thanks to increasing environmental awareness. Derived from plant-based sources, these biodegradable compounds offer a green alternative without compromising performance—at least for moderate applications.
Other types include hybrid inhibitors, which combine the strengths of multiple chemical classes, and nanotech-based solutions that offer precise targeting of scale-prone zones in complex systems.
Key Applications of Scale Inhibitors
Oil & Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry is one of the most prominent users of scale inhibitors. These inhibitors play a crucial role in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations. In the upstream segment, particularly during drilling and enhanced oil recovery (EOR), scale formation in wellbores, tubing, and surface facilities is a constant challenge due to the mixing of incompatible waters. Scale inhibitors prevent blockages and ensure a continuous flow of oil and gas.
In midstream operations, scale inhibitors maintain pipeline efficiency, reducing the risk of costly repairs or replacements. The downstream sector, which includes refineries and petrochemical plants, also relies on these chemicals to maintain smooth operations of heat exchangers and boilers.
What makes the use of scale inhibitors even more critical here is the high-pressure, high-temperature environments, where conventional cleaning methods are either too expensive or practically impossible. With millions on the line in operational downtime, the proactive use of scale inhibitors is a no-brainer for oil companies. In offshore rigs, where every square meter is vital and maintenance access is limited, scale inhibitors are a cost-effective shield against equipment degradation.
Water Treatment Plants
In municipal and industrial water treatment facilities, scale formation is more than just a maintenance issue—it can affect public health. Scale buildup in filtration membranes, RO systems, and piping can hinder water purification processes, leading to inefficiencies or contaminated output. Enter scale inhibitors: these chemicals prevent mineral accumulation, ensuring optimal filtration performance and water quality.
Municipalities, especially in regions with hard water, incorporate inhibitors into their treatment protocols to maintain a clean water supply and minimize service disruptions. Similarly, desalination plants—which are becoming critical sources of potable water in arid regions—depend on advanced scale inhibitors to maintain the integrity of their reverse osmosis systems.
Not only do these inhibitors save energy by maintaining flow rates and pressure, but they also extend the life of equipment, reducing long-term costs. With growing water scarcity and infrastructure pressure, scale inhibitors are evolving from an optional add-on to a necessity in water treatment.
Industrial Boilers and Cooling Systems
Boilers and cooling towers are notoriously prone to scale buildup due to the constant heating and cooling cycles that exacerbate mineral precipitation. In manufacturing units, power plants, and chemical processing facilities, even a thin layer of scale can drastically reduce heat transfer efficiency, increase fuel consumption, and raise operational costs.
Scale inhibitors in these systems serve a dual function: they prevent the nucleation of crystals and also disperse existing particles, preventing them from forming coherent layers. By maintaining clean surfaces, these inhibitors contribute directly to energy conservation and emission reduction.
One of the major advantages of using scale inhibitors here is cost savings. Clean heat exchange surfaces mean less energy required for heating or cooling, directly impacting the bottom line. Moreover, reduced scale formation leads to fewer shutdowns and maintenance cycles, improving operational uptime.
Industries that use recirculating water systems particularly benefit from continuous dosing of scale inhibitors, ensuring consistent performance even under variable water qualities and operational loads.
Food and Beverage Processing
Cleanliness and operational efficiency are top priorities in the food and beverage industry, and scale inhibitors play a subtle but crucial role in maintaining both. Water is a primary ingredient and utility in this sector, used for everything from cooking and cooling to cleaning and packaging. Hard water can lead to scale deposits in steam generators, water heaters, and even processing equipment—affecting product quality and safety.
Scale inhibitors ensure that processing systems remain contamination-free and compliant with health standards. They are especially critical in dairy plants, breweries, and soft drink manufacturing units, where mineral buildup could affect flavor, consistency, and microbiological safety.
In this context, food-grade or GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) inhibitors are used—formulated to perform effectively while being non-toxic and environmentally safe. With stricter food safety regulations and the rise of clean-label manufacturing, scale inhibitors are being engineered to meet both performance and purity requirements.
As consumer expectations rise and food safety becomes non-negotiable, the demand for specialized scale inhibitors in this sector continues to grow.
Regional Analysis of the Scale Inhibitors Market
North America Market Insights
North America holds a significant share of the global scale inhibitors market, thanks to its mature oil & gas infrastructure, advanced water treatment systems, and widespread adoption of chemical treatment programs. The United States, in particular, has robust industrial activity, and scale control is a standard procedure across its various sectors.
The region’s shale boom and continued oil exploration activities, especially in Texas and the Gulf of Mexico, are primary growth drivers. Additionally, stringent regulations by the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) have accelerated the demand for environmentally safe and biodegradable inhibitors.
Another contributing factor is the modernization of municipal water systems. With many cities investing in infrastructure upgrades, the adoption of scale inhibitors is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Tech innovations such as real-time scale monitoring and automated dosing systems are also gaining traction here, pushing the region to the forefront of smart water management.
Europe Market Trends
Europe’s scale inhibitors market is shaped largely by environmental consciousness and regulatory compliance. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are not just adopting inhibitors—they're demanding that these products meet strict biodegradability and eco-toxicity standards.
The EU’s REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations have prompted manufacturers to develop safer and more sustainable chemical formulations. As a result, Europe has become a hub for innovation in green scale inhibitors.
Industrial users in Europe are increasingly integrating inhibitors into broader sustainability strategies, combining them with energy efficiency and waste reduction programs. With significant activity in the water treatment, power, and manufacturing sectors, Europe remains a lucrative and forward-thinking market.
Asia-Pacific Growth Opportunities
Asia-Pacific is witnessing explosive growth in the scale inhibitors market, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development. China and India are at the forefront, with booming energy and manufacturing sectors demanding reliable water and heat system performance.
In China, desalination and industrial water reuse projects are gaining momentum, opening doors for advanced scale inhibitor formulations. Meanwhile, India’s Smart Cities Mission and focus on improving municipal water systems are catalyzing demand in the public sector.
Moreover, APAC offers cost advantages in production and labor, making it a manufacturing hub for global chemical companies. However, environmental regulations are still catching up, and this gap presents both a challenge and an opportunity for companies willing to lead in sustainable practices.
Rest of the World Outlook
Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa represent emerging frontiers for the scale inhibitors market. The Middle East, rich in oil reserves, has a naturally high demand for scale control in exploration and processing. Water scarcity issues also push the region toward desalination, further boosting inhibitor usage.
Latin America, with its expanding manufacturing base and investments in renewable energy, is seeing increasing adoption, particularly in Brazil and Mexico. Meanwhile, Africa’s growing urban population is prompting improvements in water infrastructure, setting the stage for a long-term increase in demand.
In these regions, partnerships and local production facilities can offer strategic advantages. Global players are expected to ramp up their presence here through collaborations, technology transfer, and tailored product offerings.
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-joint-compound-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-amniotic-products-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/middle-east-and-africa-travel-beauty-retail-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-travel-beauty-retail-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-automotive-aerodynamic-market
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0
Related Posts
Medical Fixation Devices Market Set to Witness Explosiv...
nitinrrr Nov 30, -0001 0