What Makes Compressed Biogas Unique
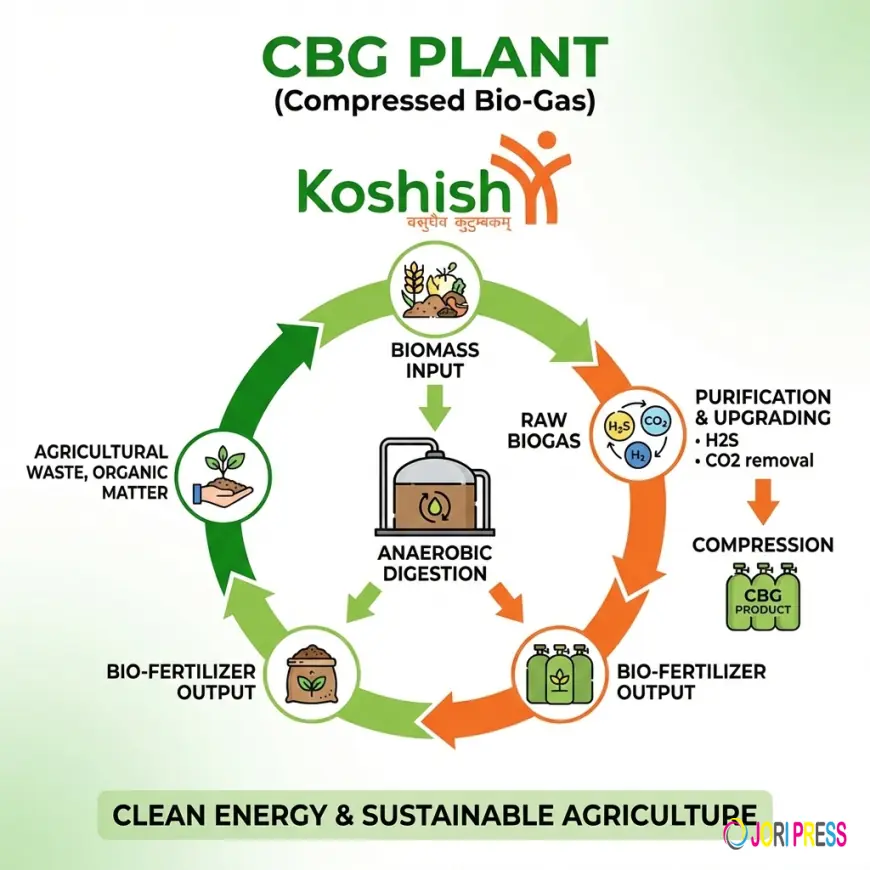
Compressed Biogas is produced by purifying and compressing biogas generated from organic materials such as agricultural waste, animal manure, food waste, and organic industrial residues. The process relies on anaerobic digestion, where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen.
The raw biogas generated contains methane along with other gases and impurities. Through purification processes, unwanted components are removed, and methane concentration is enhanced. The purified gas is then compressed, resulting in a fuel that can be used in a manner similar to conventional gas-based fuels.
Production Stages of Compressed Biogas
The production of Compressed Biogas involves a series of well-defined stages. Initially, organic waste is collected, segregated, and prepared for digestion. This feedstock is then fed into anaerobic digesters, where biological processes convert it into biogas and digestate.
The biogas is cleaned and upgraded to remove carbon dioxide, moisture, and trace contaminants. Once the desired purity is achieved, the gas is compressed and stored for distribution. The digestate produced during the process is rich in nutrients and can be used as organic fertilizer, adding value to agricultural activities.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Compressed Biogas offers significant environmental benefits. It reduces methane emissions from decomposing organic waste and lowers carbon dioxide emissions when used as a fuel. As a renewable energy source, it contributes to cleaner air and helps combat climate change.
From an economic perspective, Compressed Biogas supports energy independence by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. It creates employment opportunities in waste collection, plant operation, and maintenance. Rural areas, in particular, benefit from additional income sources through agricultural waste utilization and fertilizer production.
The use of digestate as organic manure reduces dependence on chemical fertilizers, lowering input costs for farmers and improving soil health.
Applications of Compressed Biogas
Compressed Biogas can be used across various sectors. In transportation, it serves as a cleaner alternative to conventional fuels for buses, trucks, and other gas-powered vehicles. Its compatibility with existing gas infrastructure makes adoption easier.
Industries use Compressed Biogas for heating, steam generation, and power production. Commercial establishments and institutions can also utilize it for cooking and energy needs.
In decentralized energy systems, Compressed Biogas provides reliable fuel for rural and semi-urban communities, supporting inclusive energy access.
Role in Sustainable Development
Compressed Biogas plays a key role in promoting sustainable development by integrating waste management with energy generation. It supports the circular economy by ensuring that waste materials are reused rather than discarded.
Many governments are encouraging the adoption of Compressed Biogas through supportive policies and incentives. These efforts aim to increase renewable energy capacity, reduce pollution, and promote environmentally responsible practices.
By replacing conventional fuels, Compressed Biogas helps reduce environmental degradation and supports long-term sustainability goals.
Challenges and Operational Considerations
Despite its advantages, Compressed Biogas production faces certain challenges. Setting up digestion and upgrading facilities requires significant capital investment. Consistent feedstock supply and efficient waste collection systems are essential for smooth operation.
Technical expertise and regular maintenance are critical to ensure gas quality, safety, and plant efficiency. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing awareness are helping overcome these barriers.
Future Prospects of Compressed Biogas
The future of Compressed Biogas is closely linked to global efforts toward clean energy transition. Innovations in digestion technologies, gas purification methods, and automation are improving performance and reducing costs.
As urbanization increases and waste generation grows, Compressed Biogas offers a scalable and sustainable solution. Its integration with municipal waste management systems and agricultural operations is expected to expand in the coming years.
Conclusion
Compressed Biogas represents a practical and environmentally friendly approach to meeting energy needs while addressing waste management challenges. By transforming organic waste into clean fuel and valuable by-products, it supports economic growth, environmental protection, and energy security. With continued technological progress and policy support, Compressed Biogas is set to play an increasingly important role in the renewable energy future.
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0