Designing a Functional Registration Form: HTML and CSS Basics
Basic Structure: A responsive registration form is created using HTML and CSS for styling, with a simple layout and input fields. · Form Inputs: ...
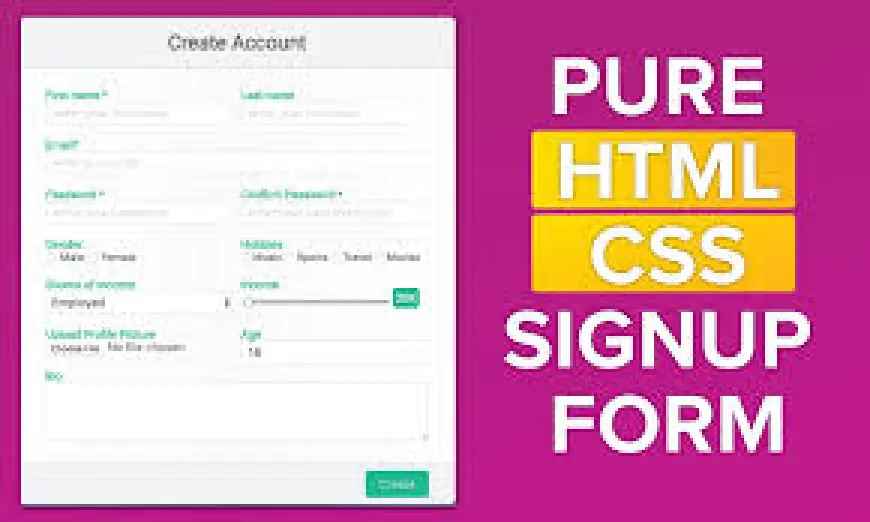
A registration form is a fundamental feature of most web applications. Whether you’re creating a signup process for a social media platform, an e-commerce site, or a blog, designing a functional and user-friendly registration form is essential. fsiblog guide to you, we’ll walk through the basics of building a registration form using HTML and CSS, focusing on fun

ctionality, design, and usability.
What Is a Registration Form?
A registration form is an interface where users provide their details to create an account on a website or app. A well-designed form ensures a smooth signup experience and collects the necessary information effectively.
Key Elements of a Registration Form:
- Text Fields: For inputs like username, email, and password.
- Labels: To describe the purpose of each field.
- Buttons: For actions like submitting or resetting the form.
- Validation: To ensure the data entered is correct.
Setting Up the Basics with HTML
HTML provides the structure of your registration form. Below is a simple example of an HTML structure for a registration form.
Basic HTML Code:
Explanation of the HTML:
- Form Tags: The
<form>element wraps the input fields and defines theaction(where the form data is sent) andmethod(how the data is sent). - Input Fields: Each input field has a
type,id, andnameattribute. For example,type="email"ensures the field accepts only email addresses. - Labels:
<label>elements provide context for each input field and improve accessibility. - Button: The
<button>element submits the form.
Styling the Form with CSS
CSS enhances the appearance of the form, making it visually appealing and easier to use. Let’s add some styles to the form.
Basic CSS for Styling:
Explanation of the CSS:
- Container Styling:
- The
.form-containerclass centers the form on the page and gives it a clean, modern look with padding, a white background, and a subtle shadow.
- The
- Input Fields:
- The
inputelements have padding and rounded corners for better aesthetics. input:focusadds a focus effect, highlighting the active field.
- The
- Button Styling:
- The
buttonhas a blue background, white text, and a hover effect for interactivity.
- The
Adding Form Validation with HTML5
HTML5 provides built-in validation attributes to ensure the form collects valid data before submission.
Validation Examples:
required: Ensures the field cannot be empty.type="email": Validates that the input is a valid email address.minlengthandmaxlength: Restrict the length of the input.pattern: Specifies a regular expression for advanced validation.
Example:
Making the Form Responsive
For a better user experience, especially on mobile devices, the form should be fully responsive.
Add CSS Media Queries:
This ensures that the form adjusts its layout and font size on smaller screens.
Enhancing the Form with Advanced Features
Once you’ve built the basic registration form, you can enhance it with additional features:
1. Custom Error Messages
Override default error messages with custom messages using JavaScript.
Example:
2. Password Visibility Toggle
Allow users to toggle password visibility for convenience.
Example:
3. Real-Time Validation
Provide instant feedback on the validity of form inputs using JavaScript.
Conclusion
Designing a functional registration form with HTML and CSS is a fundamental skill for web developers. By following the principles and examples in this guide, you can create a user-friendly, visually appealing, and responsive form for your web applications. Remember to validate user input and continually refine your design for better usability.

 jetmalsingh
jetmalsingh 










