Quantum Dots vs Traditional Nanomaterials: Key Differences and Benefits

Nanotechnology has transformed modern science by enabling the creation of materials at the nanoscale. Among these innovations, quantum dots have emerged as one of the most promising nanomaterials due to their unique optical and electronic behavior. While traditional nanomaterials such as metal nanoparticles, organic dyes, or bulk semiconductors have been used for decades, quantum dots offer new capabilities that are reshaping industries from healthcare to electronics.
This blog explains the differences between quantum dots and traditional nanomaterials and highlights why quantum dots are becoming the future of advanced technology.
What Are Quantum Dots?
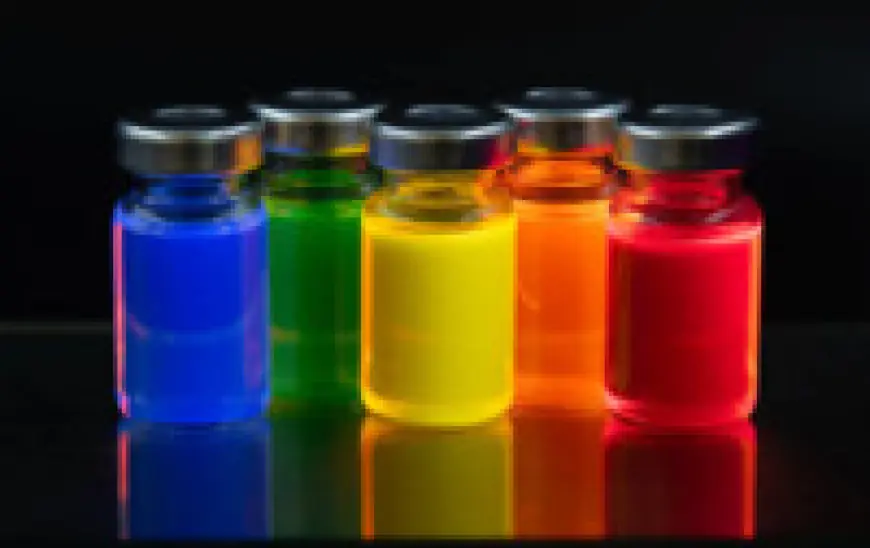
Quantum dots are extremely small semiconductor particles, typically measuring 2–10 nanometers, that exhibit unique properties because of quantum confinement effects. At this scale, electrons behave differently, allowing quantum dots to emit specific colors of light depending on their size.
One of the most important characteristics of quantum dots is size-tunable emission, meaning scientists can control the color of light simply by adjusting particle size.
These materials are widely used in:
-
Medical imaging
-
Solar cells
-
LED lighting and displays
-
Quantum computing research
-
Sensors and environmental monitoring
What Are Traditional Nanomaterials?
Traditional nanomaterials include metal nanoparticles (gold, silver), organic fluorescent dyes, and standard semiconductor nanoparticles. These materials rely mostly on surface chemistry and bulk material properties rather than quantum-level electronic behavior.
While they have been useful for catalysis, imaging, and coatings, they often lack the tunability and precision control offered by quantum dots.
Key Differences Between Quantum Dots and Traditional Nanomaterials
1. Optical Properties
The biggest difference lies in optical performance. Quantum dots have:
-
Narrow emission spectra
-
Broad absorption range
-
High brightness and color purity
Traditional dyes and nanoparticles often degrade quickly and produce broader, less precise emission signals.
Quantum dots can also be up to 20 times brighter and 100 times more stable than traditional fluorescent dyes.
2. Size-Dependent Behavior
Quantum dots exhibit strong size-dependent optical and electronic properties. For example:
-
Smaller dots → Blue/green light
-
Larger dots → Red/orange light
Traditional nanomaterials typically do not show such precise tunability based on size alone.
3. Electronic Structure
Quantum dots behave like zero-dimensional structures with discrete energy levels, giving them superior optical and electronic performance compared to bulk materials or standard nanoparticles.
This makes them useful for:
-
Quantum computing
-
High-performance sensors
-
Advanced photonic devices
4. Stability and Durability
Traditional organic dyes often suffer from photobleaching (losing brightness over time). Quantum dots, however, offer high photostability and longer operational lifetimes.
This makes them ideal for long-term medical imaging and high-end display technologies.
Benefits of Quantum Dots Over Traditional Nanomaterials
Superior Display Technology
Quantum dots provide:
-
Wider color gamut
-
Better brightness
-
Higher energy efficiency
This is why QLED televisions and modern display systems use quantum dots.
Enhanced Biomedical Applications
Quantum dots enable:
-
Real-time cell tracking
-
High-resolution imaging
-
Targeted drug delivery
Their fluorescence lifetime and stability make them far more effective than traditional dyes in biological research.
Higher Energy Efficiency
Quantum dots improve solar cell efficiency because they absorb a wider range of sunlight wavelengths.
Research suggests quantum dot solar cells could achieve significantly higher theoretical efficiency compared to traditional silicon cells.
Advanced Sensor Technology
Quantum dot sensors can detect extremely low concentrations of pollutants or biomolecules, making them valuable in environmental monitoring and diagnostics.
Challenges of Quantum Dots
Despite their advantages, quantum dots also have some limitations:
-
Some contain toxic heavy metals like cadmium
-
Manufacturing can be expensive
-
Scaling production remains challenging
However, newer materials like graphene quantum dots are being developed to reduce toxicity and cost issues.
Future of Quantum Dots in Nanotechnology
The future of quantum dots looks extremely promising. Scientists are exploring their use in:
-
Quantum computing
-
Next-generation medical diagnostics
-
Smart sensors
-
Sustainable energy solutions
As manufacturing improves and safer materials are developed, quantum dots are expected to replace many traditional nanomaterials in advanced applications.
Conclusion
The comparison between quantum dots vs traditional nanomaterials clearly shows why quantum dots are gaining attention across industries. Their tunable optical properties, high stability, and superior electronic behavior make them far more versatile than conventional nanoparticles or dyes.
As research continues, quantum dotswill likely play a major role in shaping future technologies, from medical breakthroughs to advanced electronics and clean energy solutions. Their ability to combine precision, efficiency, and versatility makes them one of the most important materials in modern nanotechnology.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0