Why Oral Cancer Screenings Are a Life-Saving Part of Your Dental Checkup
Oral cancer screenings during dental checkups in Leesburg help detect early signs and protect your health with simple preventive care.
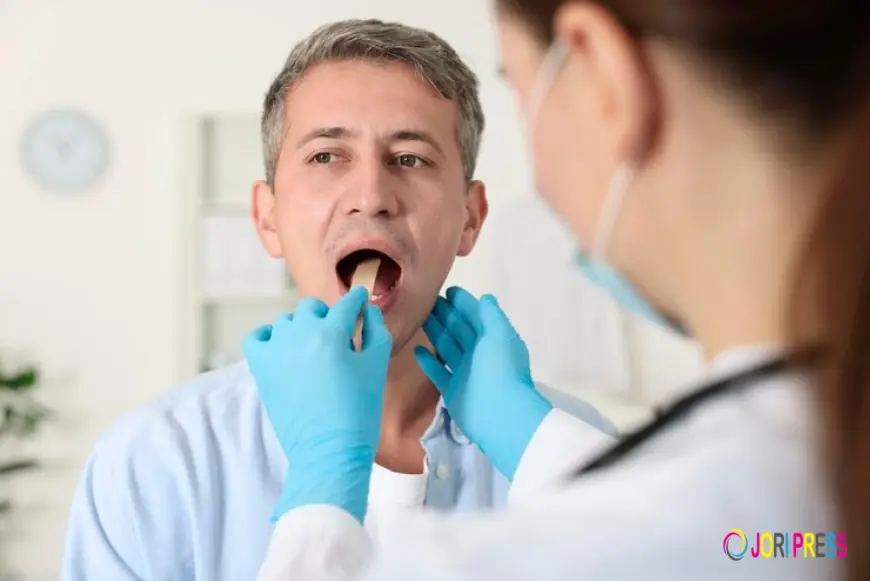

Your dental checkup is about much more than just keeping your teeth clean and cavity-free. It is an essential part of protecting your overall health. Modern dentistry focuses heavily on prevention, identifying potential problems early before they become serious, painful, or costly to treat. One of the most important yet often overlooked parts of preventive dental care is the oral cancer screening.
Oral cancer can develop quietly, sometimes without obvious pain or symptoms in its early stages. This is why routine dental visits play such a vital role. Dentists are trained not only to care for teeth and gums but also to examine the soft tissues of the mouth, tongue, lips, and throat for any unusual changes. Catching issues early can make a life-saving difference. Preventive dental care, including oral cancer screenings, gives patients peace of mind and a powerful line of defense against serious health conditions.
The Importance of Preventive Dental Care
Preventive dental care is built on a simple but powerful idea: it is always better to prevent a problem than to treat one after it has progressed. Regular dental visits allow professionals to detect early signs of tooth decay, gum disease, infections, and other oral health issues before they become severe. These visits also include professional cleanings that remove plaque and tartar buildup, helping maintain a healthy mouth and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Beyond teeth and gums, preventive care also supports your general health. Research continues to show strong links between oral health and conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues. By keeping your mouth healthy and attending regular checkups, you are investing in your whole-body wellness. Oral cancer screenings are a key part of this preventive approach, ensuring that any abnormal tissue changes are identified as early as possible.
Why Oral Cancer Awareness Matters Today
Oral cancer is a serious condition that affects thousands of people each year, and awareness is more important now than ever. While many people associate oral cancer primarily with tobacco use, other risk factors such as alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV), sun exposure to the lips, and even genetics can increase risk. Because symptoms can be subtle in the early stages, individuals may not realize something is wrong until the disease has advanced.
Early detection dramatically improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. When oral cancer is found early, it is often easier to treat and less likely to spread to other areas. This is why raising awareness about oral cancer screenings is so important. A simple, painless check performed during your regular dental visit can potentially identify warning signs before they become life-threatening. By understanding the risks and making screenings a routine part of dental care, patients take an active role in protecting their health and their future.
What Is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer refers to cancer that develops in the tissues of the mouth or throat. It is a type of head and neck cancer and most commonly begins in the thin, flat cells that line the lips and inside of the oral cavity. Because these tissues are constantly exposed to various environmental factors, they can be vulnerable to abnormal cell changes over time.
Definition and Areas of the Mouth It Can Affect
Oral cancer can affect several areas within and around the mouth. These include the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and the throat (pharynx). It may appear as a sore that does not heal, a lump, thickened tissue, or red or white patches inside the mouth. In some cases, changes may also occur in the voice, swallowing ability, or jaw movement.
Because oral cancer can develop in so many locations, routine screenings are essential. Dentists are trained to examine not only the teeth and gums but also these soft tissue areas, where early warning signs often appear first.
How Oral Cancer Develops
Oral cancer develops when cells in the mouth or throat undergo genetic changes that cause them to grow and divide uncontrollably. Normally, healthy cells follow a life cycle where old cells die and new cells replace them. When this process becomes disrupted, abnormal cells can accumulate and form a tumor.
These changes can be triggered by a combination of factors, including tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, HPV infection, prolonged sun exposure to the lips, and chronic irritation. Over time, if left undetected and untreated, these abnormal cells can invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body, making treatment more complex.
Oral Cancer by the Numbers
Understanding the impact of oral cancer highlights why screenings are so important. While it may not receive as much attention as other cancers, oral cancer remains a significant health concern worldwide.
Prevalence and Risk Trends
Oral cancer affects hundreds of thousands of people globally each year. Historically, it has been more common among older adults, especially those with long-term tobacco and alcohol use. However, recent trends show increasing cases among younger individuals, partly due to HPV-related cancers.
Men are statistically more likely to develop oral cancer than women, though the gap is narrowing. Lifestyle changes, increased awareness, and improved screening methods are influencing these trends, but the disease remains serious and potentially life-threatening.
Why Early Detection Is Critical
Early detection is the single most important factor in improving survival rates for oral cancer. When discovered in its early stages, treatment is often less invasive, more effective, and associated with better long-term outcomes. Patients diagnosed early typically experience higher survival rates and fewer complications compared to those diagnosed at later stages.
Unfortunately, oral cancer can go unnoticed because early symptoms may be painless or mistaken for minor issues. This is why routine dental checkups that include oral cancer screenings are so valuable. A quick examination by a dental professional can identify suspicious changes early, giving patients the best possible chance for successful treatment and recovery
What Is Oral Cancer Screening?
An oral cancer screening is a simple, quick, and painless examination performed by a dental professional to check for early signs of cancer or precancerous conditions in the mouth. It is a routine part of many dental checkups and plays a critical role in preventive healthcare. The goal of the screening is to detect abnormal tissue changes before they develop into more serious conditions.
What Happens During the Screening
During an oral cancer screening, your dentist carefully examines the inside of your mouth, including the lips, cheeks, gums, tongue, floor of the mouth, roof of the mouth, and the back of the throat. The process typically takes only a few minutes and does not require any special preparation from the patient.
Your dentist may also gently feel the jaw, neck, and lymph nodes to check for lumps, swelling, or unusual firmness that could indicate underlying concerns. Some dental offices may use additional screening tools or lights to help identify abnormal tissue, but the exam remains non-invasive and comfortable.
How Dentists Check for Signs and Symptoms
Dentists are trained to recognize subtle changes in the appearance and texture of oral tissues. During the screening, they look for discoloration, unusual patches, sores that are not healing, or thickened areas. They also assess symmetry and note any changes compared to previous visits.
If anything unusual is found, your dentist may recommend monitoring the area, performing additional tests, or referring you to a specialist for further evaluation. Early investigation ensures that any potential issues are addressed promptly and appropriately.
Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer symptoms can sometimes be mild or painless in the early stages, which is why professional screenings are so important. Being aware of warning signs can also help patients seek care sooner if something feels unusual.
Persistent Sores or Lumps
A sore in the mouth that does not heal within two weeks is one of the most common warning signs. Lumps, thickened areas, or rough spots inside the mouth or on the lips should also be evaluated. These changes may not always be painful, which can cause people to overlook them.
Red or White Patches
Unusual red patches, white patches, or a combination of both inside the mouth can signal abnormal cell changes. While these patches do not always indicate cancer, they should be examined by a dental professional to determine the cause and whether further testing is needed.
Difficulty Chewing, Swallowing, or Speaking
Pain, discomfort, or difficulty when chewing, swallowing, or speaking may indicate a problem in the mouth or throat. Changes in how your teeth fit together or a feeling that something is stuck in your throat can also be warning signs.
Unexplained Bleeding or Numbness
Bleeding in the mouth without a clear cause, as well as numbness or a loss of sensation in the tongue, lips, or other areas, should never be ignored. These symptoms may point to nerve involvement or tissue abnormalities that require professional evaluation.
Recognizing these signs and attending regular dental checkups ensures that potential issues are identified early, giving you the best chance for effective treatment and a positive outcome.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Understanding the risk factors for oral cancer helps patients make informed lifestyle choices and recognize when they may need more frequent screenings. While oral cancer can affect anyone, certain behaviors, exposures, and health conditions can significantly increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
Tobacco Use and Smoking
Tobacco use is one of the leading risk factors for oral cancer. This includes cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, and other smokeless tobacco products. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can damage the cells lining the mouth and throat, leading to genetic changes that may cause cancer over time. Long-term tobacco users are at especially high risk, and combining tobacco with alcohol further increases that risk.
Alcohol Consumption
Heavy or frequent alcohol use is another major contributor to oral cancer. Alcohol can irritate the cells in the mouth, making them more vulnerable to harmful substances, including those found in tobacco. Individuals who both smoke and drink heavily face a significantly higher risk than those who engage in only one of these habits. Moderation and awareness are key to reducing this risk.
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
The human papillomavirus, particularly certain high-risk strains, has been linked to cancers of the mouth and throat. HPV-related oral cancers are becoming more common, even among younger individuals who may not have traditional risk factors like tobacco use. Because HPV infections often do not show obvious symptoms, regular screenings are important for early detection.
Sun Exposure (Lip Cancer Risk)
Excessive exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can increase the risk of cancer on the lips, especially the lower lip. People who spend a lot of time outdoors without lip protection are more vulnerable. Using lip balm with sun protection and wearing hats can help reduce this risk.
Age and Family History
Oral cancer is more commonly diagnosed in adults over the age of 40, though it can occur at any age. A family history of cancer may also increase risk, as genetic factors can influence how the body responds to cell damage. Regular dental visits become increasingly important as individuals age, ensuring that any changes are identified early.
Why Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection is the most powerful tool in the fight against oral cancer. Because symptoms may be subtle or painless at first, routine screenings during dental visits provide a critical opportunity to identify warning signs before the disease advances.
Survival Rates with Early vs. Late Diagnosis
When oral cancer is detected in its early stages, treatment is often more successful and less invasive. Survival rates are significantly higher for early-stage diagnoses compared to cases found after the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Late-stage oral cancer may require more aggressive treatments, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, which can impact quality of life.
How Screenings Improve Treatment Outcomes
Oral cancer screenings allow dental professionals to spot suspicious changes and take action quickly. Early intervention can mean smaller tumors, less extensive treatment, and better overall recovery. Screenings also give patients peace of mind, knowing that their oral health is being monitored regularly.
By making oral cancer screenings a routine part of dental care, patients take an active role in protecting their health. A few minutes during a dental checkup can make a life-saving difference.
How Dentists Perform Oral Cancer Screenings
Oral cancer screenings are designed to be quick, comfortable, and thorough. Dentists are trained to evaluate both visible and hidden areas of the mouth and surrounding tissues to detect any unusual changes as early as possible. The process is non-invasive and is often completed during your routine dental exam.
Visual Examination of the Mouth, Tongue, and Throat
The screening begins with a careful visual inspection of the soft tissues inside your mouth. Your dentist examines the lips, gums, cheeks, tongue, floor of the mouth, roof of the mouth, and the back of the throat. They look for abnormal color changes, sores that are not healing, red or white patches, swelling, or irregular tissue textures.
The tongue is gently moved to allow the dentist to see all sides, as this area is a common site for early signs. Good lighting and dental instruments help ensure that even subtle changes are noticed.
Physical Examination of the Jaw and Neck
In addition to looking inside your mouth, your dentist will gently feel along your jawline, under your chin, and along your neck. This helps check for lumps, swelling, or enlarged lymph nodes that could signal an issue beneath the surface.
This part of the exam is important because some abnormalities cannot be seen but may be felt. It also helps assess whether there are signs that something has spread beyond the mouth.
Use of Advanced Screening Tools if Needed
In some cases, dentists may use additional tools to enhance the screening. Special lights or dyes can help highlight abnormal cells that may not be visible under standard lighting. These tools do not replace a professional evaluation but can provide extra information if an area of concern is found.
If anything unusual is detected, your dentist may recommend monitoring the area, taking photographs for comparison, or referring you to a specialist for further testing or a biopsy.
Who Should Get an Oral Cancer Screening?
Oral cancer screenings are not only for people with obvious symptoms or known risk factors. They are an important part of routine dental care for a wide range of patients.
Adults of All Ages
While oral cancer is more common in older adults, it can occur at any age. Including screenings as part of regular dental checkups ensures that changes are caught early, regardless of age. Younger adults, especially with rising HPV-related cases, also benefit from routine evaluations.
High-Risk Individuals
People who use tobacco products, consume alcohol frequently, have a history of HPV infection, spend significant time in the sun without lip protection, or have a family history of cancer should be especially diligent about screenings. These individuals may need more frequent evaluations based on their dentist’s recommendations.
Why Screenings Are Important Even Without Symptoms
One of the most important facts about oral cancer is that it can develop without pain or obvious symptoms in its early stages. Waiting until something feels wrong may mean the disease has already progressed. Routine screenings provide a proactive approach, allowing dentists to detect subtle warning signs before they become serious.
Even if you feel perfectly healthy, regular oral cancer screenings offer reassurance and an added layer of protection for your long-term health.
How Often Should You Be Screened?
Oral cancer screenings are most effective when they are part of your regular dental care routine. Because changes in the mouth can develop over time, consistent monitoring allows dental professionals to notice anything new or unusual as early as possible.
Recommended Frequency During Dental Visits
For most patients, an oral cancer screening is recommended at least once a year, often during a routine dental exam. Many dental practices include a basic screening at every checkup, which typically occurs every six months. The exact frequency may vary depending on your personal risk factors, age, and medical history. Individuals at higher risk may benefit from more frequent evaluations, as advised by their dentist.
Importance of Regular Checkups
Regular dental visits do more than keep your teeth clean. They create an ongoing record of your oral health, making it easier to detect even small changes in tissue, color, or texture. A dentist who sees you consistently is more likely to notice subtle differences that could signal an early issue. Skipping checkups means missing these opportunities for early detection, which can delay diagnosis and treatment if a problem develops.
What Happens If Something Suspicious Is Found?
Finding an unusual spot or change during a screening does not automatically mean cancer. Many oral abnormalities are harmless or related to minor irritation. However, any suspicious area should be evaluated carefully to rule out serious conditions.
Follow-Up Steps
If your dentist notices something concerning, they may first choose to monitor the area for a short period to see if it heals on its own, especially if it could be caused by irritation or injury. They may document the area with notes or photographs to track any changes. If the spot does not improve or shows signs that require further investigation, additional steps will be recommended.
Biopsy and Referral Process
When necessary, your dentist may refer you to a specialist, such as an oral surgeon or ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctor, for further evaluation. A biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of tissue for laboratory testing, may be performed to determine whether cancerous or precancerous cells are present. This procedure is typically quick and done with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Importance of Not Panicking but Acting Promptly
It is natural to feel worried if something unusual is found, but staying calm is important. Many abnormalities turn out to be noncancerous. The key is to follow your dentist’s recommendations and address the issue promptly. Early evaluation allows for faster answers and, if needed, early treatment, which greatly improves outcomes. Taking action quickly provides the best chance for protecting your health while avoiding unnecessary stress.
The Role of Your Dentist in Preventive Health
Your dentist plays a much bigger role in your well-being than many people realize. While dental visits are often associated with cleanings and cavity checks, modern dentistry is deeply connected to preventive healthcare. Dentists are trained to look beyond teeth and gums, identifying early signs of conditions that can affect your entire body, including oral cancer, infections, and other systemic health issues.
Dentistry Beyond Teeth and Gums
The mouth is closely linked to the rest of the body, and changes in oral tissues can sometimes signal broader health concerns. During routine exams, dentists examine the tongue, cheeks, throat, jaw, and surrounding structures, checking for abnormalities that may otherwise go unnoticed. They also monitor gum health, which has been connected to conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
Oral cancer screenings are a powerful example of how dentistry extends beyond basic oral care. By evaluating the soft tissues of the mouth and neck, dentists help detect serious conditions early, often before symptoms appear. This preventive approach transforms dental visits into an essential part of maintaining total-body health.
Protecting Your Overall Health
Preventive dental care supports your immune system, reduces the risk of infections, and helps maintain proper nutrition by keeping your mouth healthy and pain-free. Early detection of oral issues can prevent complications that may impact speech, eating, and overall quality of life.
By attending regular dental checkups, patients create a partnership with their dental provider focused on long-term wellness. Your dentist becomes an important ally in protecting not only your smile but also your general health, offering guidance, screenings, and early intervention when needed.
Conclusion
Oral cancer screenings are a simple yet life-saving part of routine dental care. They take only a few minutes, cause no discomfort, and provide invaluable insight into your health. Because oral cancer can develop silently, these screenings offer a critical opportunity to catch warning signs early, when treatment is most effective.
Understanding the risk factors, recognizing potential symptoms, and committing to regular dental visits empower you to take control of your health. Your dentist is not just caring for your teeth, they are helping safeguard your future. By making oral cancer screenings a consistent part of your dental checkups, you are investing in early detection, peace of mind, and a healthier life overall.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0