Introduction to Plumbing Design: Everything You Need to Know
This article provides a comprehensive introduction to plumbing design, covering its importance, components, processes, standards, and future trends. By the end, you’ll understand why plumbing design is the backbone of every successful construction project.
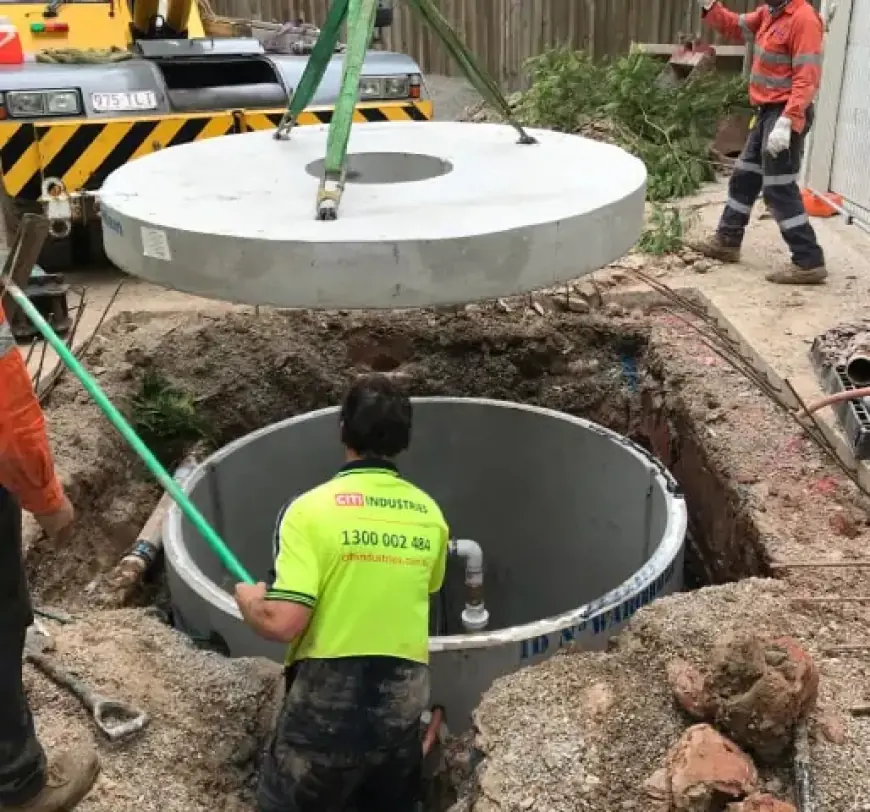

Plumbing design is one of the most critical aspects of building construction, whether for residential, commercial, or industrial projects. A well-thought-out plumbing system ensures efficient water supply, effective drainage, and reliable wastewater management, all while adhering to safety standards and environmental regulations. Without proper plumbing design, buildings can face recurring issues such as leaks, water pressure problems, drainage failures, or even structural damage caused by water infiltration.
This article provides a comprehensive introduction to plumbing design, covering its importance, components, processes, standards, and future trends. By the end, you’ll understand why plumbing design is the backbone of every successful construction project.
What is Plumbing Design?
Plumbing design refers to the systematic planning and layout of a building’s water supply, drainage, and venting systems. It involves determining the placement of pipes, fixtures, valves, pumps, and other essential components to ensure the seamless distribution of clean water and the safe disposal of wastewater.
A plumbing design must balance functionality, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with local building codes. Engineers and designers must also anticipate future maintenance needs and environmental impacts.
Why Plumbing Design is Important
- Water Efficiency
A good plumbing design reduces water wastage by optimizing pipe sizes, layouts, and fixtures. This is especially important in regions facing water scarcity. - Cost Savings
Well-planned systems reduce installation costs, minimize material wastage, and lower long-term maintenance expenses. - Health and Safety
Plumbing design prevents cross-contamination between clean water and wastewater. Proper drainage avoids stagnant water, which can cause health hazards. - Sustainability
Modern plumbing design incorporates energy-efficient pumps, rainwater harvesting, and greywater recycling, making buildings more eco-friendly. - Compliance with Standards
Adhering to building codes and regulations ensures legal compliance and guarantees the safety and durability of the system.
Key Components of Plumbing Design
A plumbing design consists of several interconnected systems that work together to ensure smooth operation. The major components include:
1. Water Supply System
This system delivers clean, potable water from the source to various fixtures. It includes:
- Water meters and pumps
- Pipes and valves
- Pressure regulators
- Storage tanks
2. Drainage System
The drainage network removes wastewater and stormwater from the building. Key elements are:
- Drain pipes
- Traps and vents
- Sewer connections
- Sump pumps
3. Vent System
Vent pipes allow gases to escape and ensure proper air circulation, preventing negative pressure in drains that could cause blockages or foul odors.
4. Fixtures and Appliances
These include sinks, showers, toilets, dishwashers, and washing machines. The placement of fixtures greatly impacts the efficiency of the plumbing system.
5. Hot Water System
This involves heaters, boilers, or solar heating units that supply hot water for domestic or industrial use.
The Plumbing Design Process
Plumbing design is not just about drawing pipe layouts; it’s a structured process that requires careful planning and engineering. The major steps include:
- Requirement Analysis
Designers first assess the building’s needs, considering the number of occupants, types of activities, and local water availability. - Preliminary Layout
An initial design draft identifies the location of fixtures, water sources, drainage outlets, and major pipelines. - Pipe Sizing and Material Selection
The diameter and material of pipes are chosen based on water pressure requirements, flow rate, and durability. Common materials include copper, PVC, PEX, and stainless steel. - Hydraulic Calculations
Engineers calculate water pressure, flow rates, and pump requirements to ensure the system operates efficiently. - Code Compliance
The design must follow local building codes, plumbing standards, and safety regulations. - Final Design and Documentation
Detailed drawings and blueprints are prepared for contractors and installers. - Installation and Testing
Once implemented, the system undergoes pressure and leak testing before becoming operational.
Plumbing Design Standards and Codes
Every region follows specific plumbing standards to ensure safety and efficiency. Some widely recognized codes include:
- Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC)
- International Plumbing Code (IPC)
- National Standard Plumbing Code (NSPC)
- Local building codes and municipal guidelines
These standards dictate pipe sizes, materials, installation methods, and safety practices. Compliance is non-negotiable to avoid legal and operational issues.
Challenges in Plumbing Design
Despite technological advancements, plumbing design still faces challenges such as:
- Water Scarcity: Designing systems that reduce water consumption.
- Aging Infrastructure: Replacing outdated pipes and fixtures in older buildings.
- Urban Density: Managing complex plumbing networks in high-rise structures.
- Environmental Concerns: Minimizing water pollution and conserving natural resources.
- Cost Constraints: Balancing budget limitations with quality and durability.
Future Trends in Plumbing Design
The plumbing industry is evolving rapidly, with new innovations improving efficiency, sustainability, and user experience. Some trends to watch include:
- Smart Plumbing Systems
IoT-enabled sensors that monitor leaks, water pressure, and consumption in real time. - Green Plumbing Solutions
Increased adoption of greywater recycling, rainwater harvesting, and low-flow fixtures. - 3D Modeling and BIM Integration
Using Building Information Modeling (BIM) to visualize and coordinate plumbing systems with other building services. - Energy-Efficient Hot Water Systems
Solar water heaters, heat pump systems, and tankless water heaters are becoming more common. - Advanced Materials
High-performance, corrosion-resistant materials like PEX and composite piping are replacing traditional metal systems.
Conclusion
Plumbing design is much more than just fitting pipes and fixtures. It’s a meticulous engineering process that ensures a building’s water supply and drainage systems operate efficiently, safely, and sustainably. From residential homes to high-rise towers, the success of every structure relies heavily on a well-planned plumbing design.
As technology advances and environmental concerns grow, plumbing design will continue to evolve, adopting smarter systems and greener solutions. For architects, engineers, and builders, understanding plumbing design is essential to creating functional, durable, and future-ready buildings.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0