How to Do Sugarcane Farming in India from Start to Finish
Sugarcane, or Saccharum officinarum, is a profitable crop in India. It is not only used for sugar production, but it is also an important raw material for industries like paper, ethanol, and chemicals.
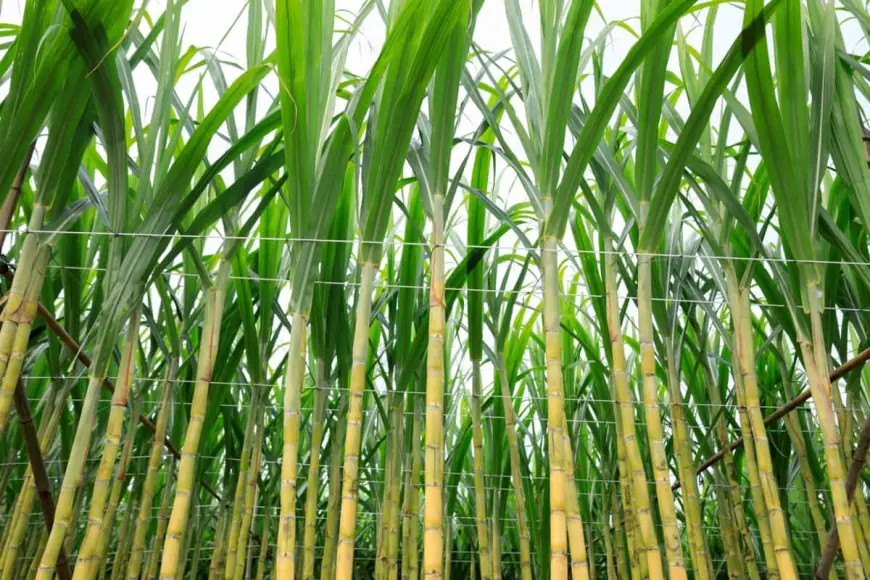

Sugarcane, or Saccharum officinarum, is a profitable crop in India. It is not only used for sugar production, but it is also an important raw material for industries like paper, ethanol, and chemicals. While sugarcane farming is relatively simple, it still requires significant preparation due to its long harvesting period.
So, if you are planning to start sugarcane farming in India, you will need to make substantial preparations based on the sugarcane variety and the region’s climate. Here’s a comprehensive guide to get you started with sugarcane farming in 2025.
This guide will help you with land preparation, variety selection, harvesting, and choosing the right tractor for efficient farm operations:
Step-by-Step Guide to Start Sugarcane Farming in India
India is the world’s second-largest sugarcane producer after Brazil. Uttar Pradesh has the highest sugarcane production output, followed by Maharashtra. Sugarcane can be easily grown alongside other crops, allowing farmers to diversify their farming operations. Crop diversification helps enhance crop yield, improve soil fertility, and reduce pest attacks.
Here’s everything you need to know to do sugarcane farming in India:
Land Preparation
Sugarcane needs deep and fertile soil, mostly loamy soil with good drainage. The sugarcane field needs to be deeply ploughed 2-4 times using a rotavator and cultivator. Ploughing helps clear the field and eliminate weeds.
Then the field will need to be harrowed and levelled using implements like a disc harrow and leveller. Levelling ensures equal water distribution and prevents waterlogging in the field.
You should utilise heavy-duty tractor models, like John Deere 5310 Trem IV 4WD or Mahindra Arjun Novo 605 DI-i 4WD, to operate implements. The John Deere tractor model, for instance, provides 57 HP and a 2500 Kg lifting capacity, which ensures efficient handling of agricultural implements.
Seed Selection and Preparation
There are many sugarcane varieties available, like Kalyani, Bhavani, Moti, Krishna, Raseeli, and Nayana. Choosing the right seed based on the climatic conditions and soil type is crucial.
For instance, varieties like Co 0238, Co 0118, and Co 05011 are considered suitable for North Indian states like Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Bihar, because of the subtropical climate.
For the seed preparation, follow these steps:
-
Select a healthy seed cane from a disease-free field that is 7-9 months old.
-
Cut the canes into small pieces called “setts.”
-
Soak is set in a solution of Bavistin (Carbendazim) 0.1% or Thiram 0.25% for 10–15 minutes for fungicide treatment.
-
Dry them before planting.
Plantation Time
Sugarcane takes 12-14 months to mature in sub-tropical states like Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, and others. It may also take up to 18 months to mature in tropical states like Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Sugarcane can be planted twice a year:
-
Autumn period (September to October)
-
Spring period (February to March)
Irrigation and Fertiliser
Sugarcane is an extremely water-intensive crop. It takes approximately 25,000 kg of water to produce 100 kg of sugarcane. Therefore, maintaining optimal soil moisture throughout the growth period is important to ensure maximum yield. The water requirement of the sugarcane crop varies based on region (inclusive of rainfall):
-
Tropical India: from 2000 to 3000 mm
-
Sub-tropical India: from 1400 to 1800 mm
In case of low rainfall, an appropriate irrigation system should be installed to ensure soil moisture and prevent crop damage. You should follow the irrigation schedule given below for timely irrigation:
-
Germination Phase: Once every 7 days
-
Tillering Phase: Once every 10 days
-
Growth Phase: Once every 7 days
-
Maturity Phase: Once every 15 days
Urea should be used to fulfil the nitrogen requirements on sugarcane farms. However, the nitrogen requirements differ for different regions based on the soil type and climate.
Weed and Pest Control
Effective weed and pest control in sugarcane farming is essential for healthy crop growth and higher yield. Farmers should remove weeds manually or use inter-row cultivators during the first 45–60 days after planting.
Common pests like shoot borers and aphids can be managed by spraying insecticides such as Chlorpyriphos or Imidacloprid. Using a Swaraj tractor with a sprayer or cultivator attachment makes the weeding and pest control process quicker and more efficient.
Harvesting
Sugarcane harvesting begins when the crop matures, usually after 10–12 months, and the canes show signs like dry lower leaves and a solid, sweet stalk. Farmers should harvest early in the morning using a sickle or mechanical cutter for best results.
Then, transport the harvested sugarcane to the mill within 24 to 36 hours for better sugar recovery. Using a tractor with a trolley ensures quick transport and reduces post-harvest losses. For small to mid-sized farms, tractors at a competitive price offer a reliable solution for managing harvesting and haulage operations effectively.
Swaraj tractor price in India, for instance, ranges from Rs. 2.60 lakh to Rs. 14.31 lakh. These tractors can efficiently perform various field operations required in sugarcane cultivation, like ploughing, tilling, and inter-row cultivation.
Conclusion
Sugarcane farming is a profitable business for farmers, as the crop is easy to maintain and provides a high yield with dedicated efforts. The right preparation strategy for sugarcane cultivation will help you achieve better crop health, higher productivity, and a timely return. With proper planning, disease control, and use of suitable machinery, sugarcane farming can become a sustainable and consistent source of income for farmers.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0