Advantages of Quantum Dots Nanoparticles Over Traditional Nanomaterials

Nanotechnology has transformed modern science by enabling materials to function at atomic and molecular scales. Among the many innovations in this field, quantum dots nanoparticles stand out as one of the most advanced and versatile nanomaterials available today. While traditional nanomaterials such as metal nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, and bulk semiconductor nanostructures have played a significant role in technological progress, quantum dots offer unique advantages that push performance, precision, and efficiency to a new level.
This blog explores the key advantages of quantum dots nanoparticles over traditional nanomaterials and why they are increasingly preferred across industries such as electronics, healthcare, energy, and imaging.
What Are Quantum Dots Nanoparticles?
Quantum dots nanoparticles are ultra-small semiconductor particles, typically ranging from 2 to 10 nanometers in size. At this scale, they exhibit quantum mechanical properties, meaning their optical and electronic behavior can be precisely controlled by simply adjusting their size and composition. This size-dependent behavior sets them apart from traditional nanomaterials, whose properties are often fixed and less tunable.
1. Superior Optical Properties
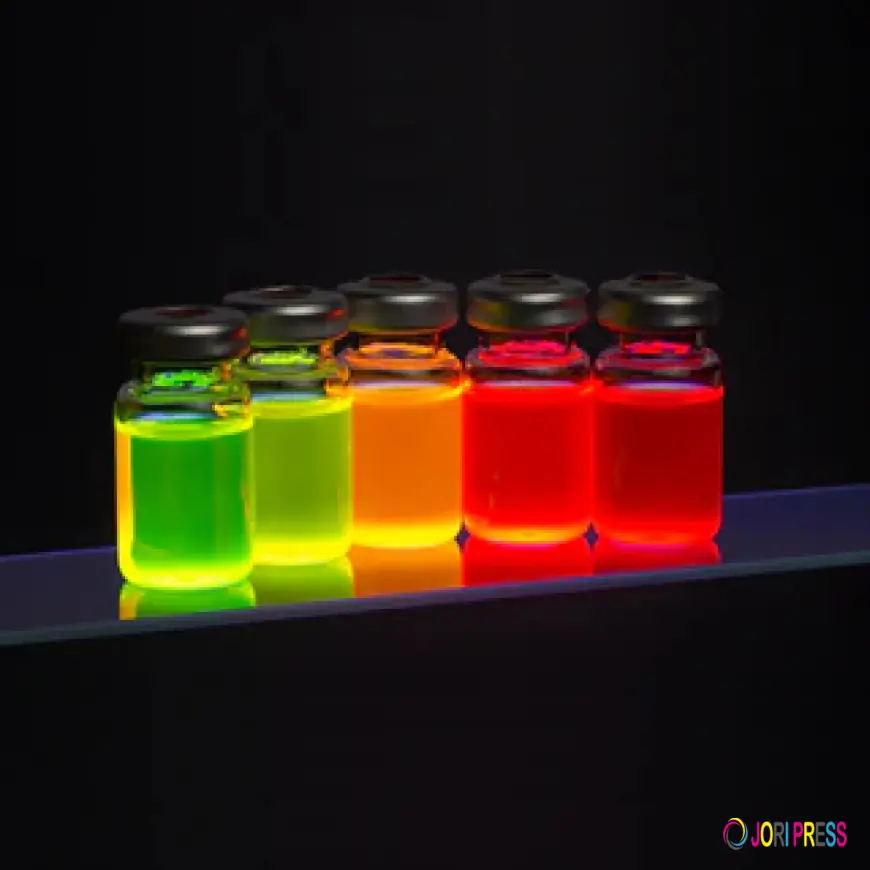
One of the biggest advantages of quantum dots nanoparticles is their exceptional optical performance. Unlike traditional nanomaterials that may emit broad or unstable light spectra, quantum dots produce highly pure, narrow, and tunable emission
By changing the size of a quwavelengths.antum dot, scientists can control the color of light it emits—without altering its chemical composition. This precision makes quantum dots far superior for applications such as:
-
High-definition displays (QLED TVs)
-
Fluorescent bioimaging
-
Advanced optical sensors
Traditional nanomaterials often lack this level of color accuracy and consistency.
2. High Brightness and Stability
Quantum dots nanoparticles exhibit remarkable brightness and photostability compared to conventional nanomaterials. They resist photobleaching, meaning they maintain their brightness even after prolonged exposure to light.
In contrast, organic dyes and some traditional nanoparticles degrade over time, limiting their long-term usability. This enhanced stability makes quantum dots ideal for applications requiring continuous or long-term performance, such as medical diagnostics, imaging, and lighting technologies.
3. Size-Tunable Electronic Properties
Another major advantage of quantum dots nanoparticles is their size-dependent electronic behavior. As their size decreases, the energy gap increases, allowing precise tuning of electrical conductivity and absorption properties.
Traditional nanomaterials generally require chemical modification or complex processing to alter their electronic properties. Quantum dots, however, achieve this naturally through size control, offering:
-
Greater design flexibility
-
Lower material modification costs
-
Higher performance efficiency
This makes them highly attractive for use in transistors, sensors, and next-generation semiconductors.
4. Enhanced Performance in Biomedical Applications
Quantum dots nanoparticles have revolutionized biomedical research and healthcare due to their superior imaging and targeting capabilities. Their small size allows them to interact efficiently with biological systems, while their strong fluorescence enables highly accurate imaging.
Compared to traditional nanomaterials, quantum dots offer:
-
Improved imaging contrast
-
Longer imaging duration
-
Multiplexing capabilities (detecting multiple targets simultaneously)
These advantages are especially valuable in cancer diagnostics, cellular imaging, drug delivery, and biosensing applications.
5. Higher Energy Efficiency
In energy-related applications, quantum dots nanoparticles outperform many traditional nanomaterials by enabling more efficient light absorption and energy conversion. Their tunable bandgap allows them to capture a broader spectrum of light, making them highly effective in:
-
Solar cells
-
Photodetectors
-
Light-harvesting systems
Traditional nanomaterials often absorb a limited range of wavelengths, resulting in lower overall efficiency. Quantum dots help overcome this limitation, leading to improved performance and reduced energy loss.
6. Improved Integration with Modern Technologies
Quantum dots nanoparticles are easier to integrate into modern manufacturing processes compared to some traditional nanomaterials. They can be incorporated into thin films, inks, polymers, and coatings without compromising performance.
This compatibility enables their use in flexible electronics, wearable devices, and advanced coatings—applications where traditional nanomaterials may struggle due to rigidity or processing constraints.
7. Scalability and Commercial Potential
With advancements in synthesis techniques, quantum dots nanoparticles are becoming increasingly scalable and cost-effective. While traditional nanomaterials often require complex fabrication processes, quantum dots can now be produced with high consistency and uniformity.
This scalability has accelerated their commercial adoption in consumer electronics, healthcare devices, and renewable energy solutions.
Conclusion
Quantum dots nanoparticles represent a significant leap forward in nanotechnology. Their superior optical properties, tunable electronic behavior, enhanced stability, and broad application potential give them a clear advantage over traditional nanomaterials. From high-performance displays and medical imaging to renewable energy and advanced electronics, quantum dots are shaping the future of innovation.
As research and manufacturing techniques continue to evolve, quantum dots nanoparticles are expected to replace or enhance many traditional nanomaterials, offering smarter, more efficient, and more adaptable solutions across industries.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0