Privacy-First Smart Contracts Using Homomorphic Encryption
Explore how privacy-first smart contracts using homomorphic encryption are transforming secure blockchain applications. Learn how smart contract development companies and services enable confidential, compliant, and automated workflows for enterprises in 2025.
In the modern blockchain ecosystem, privacy remains a critical concern. Traditional smart contracts, while transparent and secure, often expose sensitive transaction details and business logic on public ledgers. This lack of confidentiality can hinder adoption among enterprises and startups dealing with sensitive financial, healthcare, or personal data. Privacy-first smart contracts, leveraging advanced cryptographic techniques such as homomorphic encryption, are transforming the landscape by allowing computations on encrypted data without revealing the underlying information. Leading smart contract development companies and specialized smart contract development services are enabling businesses to implement these solutions effectively, balancing transparency, security, and privacy.
Understanding Privacy Challenges in Smart Contracts
Standard smart contracts operate on public blockchains, where all contract code and transaction data are visible to network participants. While this ensures transparency and immutability, it also exposes proprietary logic, sensitive financial details, and user data. Enterprises, particularly in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management, often require privacy guarantees that traditional smart contracts cannot provide.
Privacy-first smart contracts aim to address these challenges by employing encryption methods that maintain confidentiality while preserving the ability to execute contract logic. Homomorphic encryption stands out as a key innovation, enabling computations directly on encrypted data without decryption. This approach allows businesses to execute complex workflows while keeping sensitive information secure.
What is Homomorphic Encryption?
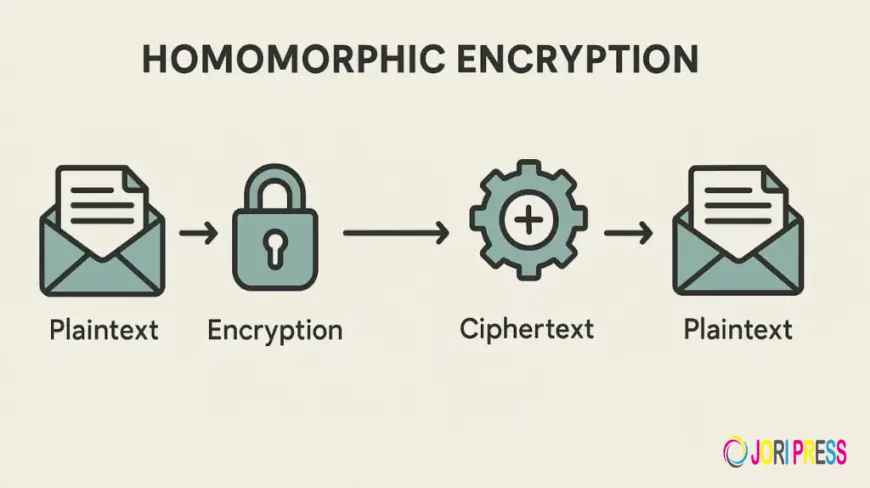
Homomorphic encryption is a cryptographic technique that allows operations to be performed on encrypted data, producing results that, when decrypted, match the outcome of operations performed on plaintext data. In the context of smart contracts, this means sensitive inputs such as payroll details, bidding information, or medical records can be processed without ever exposing the raw data on the blockchain.
This ability to compute on encrypted data transforms privacy-sensitive applications, allowing organizations to maintain confidentiality while benefiting from blockchain’s transparency and immutability. Homomorphic encryption can be partial (supporting addition or multiplication) or fully homomorphic (supporting arbitrary computations), depending on the use case.
Implementing Privacy-First Smart Contracts
Encrypted Data Inputs
Smart contracts can accept encrypted inputs from users, businesses, or IoT devices. These inputs are never exposed on-chain in plaintext, ensuring that confidential information such as salaries, financial metrics, or proprietary algorithms remain hidden from all parties, including the network validators.
Secure Computation and Validation
Using homomorphic encryption, the smart contract executes operations directly on encrypted data. Validators on the blockchain can confirm that the computations are correct without accessing the underlying data. This preserves both the integrity of the computation and the privacy of participants.
Integration with Existing Systems
Privacy-first smart contracts can integrate with enterprise databases, ERP systems, and secure off-chain data sources. This hybrid approach enables companies to adopt blockchain solutions without overhauling their existing IT infrastructure, maintaining seamless workflows while gaining enhanced privacy.
Key Management and Access Control
Proper key management is essential for privacy-first smart contracts. Only authorized parties should possess the decryption keys necessary to interpret results. Advanced access control mechanisms, combined with encryption, ensure that sensitive outputs remain protected and are only accessible to permitted stakeholders.
Use Cases of Privacy-First Smart Contracts
Financial Services
Banks and fintech firms can process loan applications, credit scoring, and risk assessments on encrypted customer data. This ensures compliance with regulations such as GDPR while maintaining data privacy.
Healthcare
Smart contracts can automate insurance claims, patient record management, and clinical trial workflows while keeping sensitive medical information encrypted and confidential.
Supply Chain Management
Companies can manage proprietary supplier data, inventory levels, and pricing agreements without exposing confidential information on public ledgers, enhancing both privacy and competitiveness.
Decentralized Voting and Governance
Homomorphic encryption enables secure, verifiable voting in DAOs or corporate governance platforms, preserving voter anonymity while ensuring accurate tallying of results.
Confidential Auctions and Marketplaces
Smart contracts can manage sealed-bid auctions, competitive pricing, and other sensitive financial transactions without revealing participant bids or strategies, maintaining fairness and confidentiality.
Technical Considerations for Deployment
Choosing the Right Encryption Scheme
The choice between partially homomorphic and fully homomorphic encryption depends on the complexity of the computation and performance requirements. Fully homomorphic encryption supports arbitrary computations but may introduce latency and higher computational costs.
Performance and Scalability
Processing encrypted data is computationally intensive. Smart contract developers must optimize algorithms, consider layer-2 solutions, or employ hybrid architectures that balance on-chain privacy with off-chain computation for efficiency.
Security Auditing
Given the complexity of privacy-first smart contracts, audits by experienced smart contract development companies are critical. Audits ensure that encryption is correctly implemented, keys are securely managed, and potential vulnerabilities are addressed.
Regulatory Compliance
Privacy-first smart contracts must align with global privacy and data protection regulations. Incorporating built-in compliance features, such as selective disclosure of encrypted data, ensures legal adherence while maintaining confidentiality.
Advantages of Privacy-First Smart Contracts
Confidentiality
Sensitive business and user data remain encrypted, reducing exposure and safeguarding proprietary information.
Trust and Compliance
Participants can trust the system because computations are verifiable on-chain without exposing private data, aiding compliance with privacy regulations.
Security
Encryption adds an additional layer of protection against malicious actors, hacking attempts, or insider threats.
Flexibility
Smart contracts can handle various confidential workflows across industries, from finance to healthcare to governance, enhancing adaptability.
Enhanced Adoption
By addressing privacy concerns, enterprises are more likely to adopt blockchain solutions for critical business processes.
Future Trends in Privacy-First Smart Contracts
AI-Enhanced Encrypted Computation
Artificial intelligence can process encrypted datasets for predictive analytics, risk management, and automation without exposing sensitive information.
Interoperability Across Blockchains
Privacy-first smart contracts will increasingly interact across multiple blockchain networks, enabling confidential workflows spanning diverse platforms.
Tokenized Confidential Assets
Sensitive assets can be tokenized and managed via encrypted smart contracts, allowing secure trading, lending, or staking without revealing asset details.
Real-Time Privacy Audits
Advanced smart contract frameworks may incorporate real-time privacy audits to verify that data handling and encryption standards are continuously maintained.
Scalable Homomorphic Protocols
Ongoing research will make fully homomorphic encryption more computationally efficient, enabling wider adoption in high-frequency smart contract applications.
Conclusion
Privacy-first smart contracts leveraging homomorphic encryption are poised to redefine blockchain applications by offering secure, confidential, and compliant workflows. Businesses engaging smart contract development services from expert
smart contract development company can implement these solutions to protect sensitive data, automate complex processes, and enhance trust across stakeholders. From finance and healthcare to supply chain and governance, privacy-first smart contracts are enabling a new era of secure, scalable, and enterprise-ready blockchain solutions.
Visit our website -wisewaytec.com
FAQs
Q1. What makes smart contracts privacy-first?
Privacy-first smart contracts use encryption, such as homomorphic encryption, to process data without revealing sensitive information on the blockchain.
Q2. How does homomorphic encryption work in smart contracts?
It allows computations to be performed directly on encrypted data, producing results that, when decrypted, match operations performed on plaintext.
Q3. Which industries benefit from privacy-first smart contracts?
Financial services, healthcare, supply chain management, decentralized governance, and confidential marketplaces are prime beneficiaries.
Q4. How can businesses implement these smart contracts securely?
Through professional smart contract development companies, ensuring encryption, key management, and audits are properly executed.
Q5. What are the future trends in privacy-first smart contracts?
AI-enhanced encrypted computation, cross-chain interoperability, tokenized confidential assets, and scalable homomorphic protocols are key emerging trends.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0