Genetic Testing in Pregnancy: What Every Parent-to-Be Should Know
One of the most valuable tools available today is genetic testing during pregnancy. These tests provide crucial insights into the baby’s development and can help detect potential genetic conditions early on.
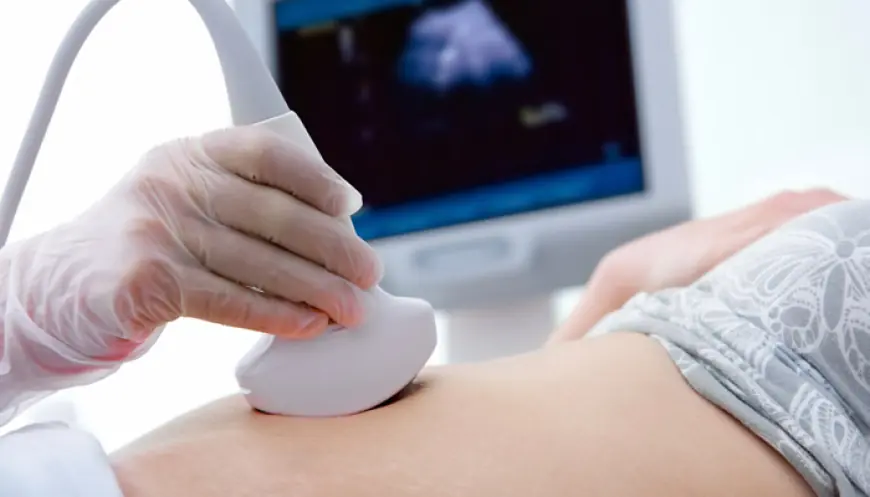
Pregnancy is an exciting journey, but it also comes with important health checks to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby. One of the most valuable tools available today is genetic testing pregnancy. These tests provide crucial insights into the baby’s development and can help detect potential genetic conditions early on.
What Is Genetic Testing in Pregnancy?
Genetic testing in pregnancy refers to medical tests that analyse the baby’s DNA or chromosomes to identify possible genetic or chromosomal abnormalities. These tests help doctors detect conditions like Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, and certain inherited disorders.
Types of Genetic Tests in Pregnancy
-
Screening Tests
-
These estimate the risk of the baby having certain conditions. They do not provide a definite diagnosis but indicate whether further testing is needed.
-
Examples:
-
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): A blood test from the mother that examines fragments of the baby’s DNA.
-
First Trimester Screening: Combines blood tests with ultrasound to assess chromosomal conditions.
-
-
-
Diagnostic Tests
-
These provide a clear, definitive result and are usually recommended if screening tests show a higher risk.
-
Examples:
-
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): A sample of placental tissue is tested (done between 10–13 weeks).
-
Amniocentesis: A sample of amniotic fluid is tested (done between 15–20 weeks).
-
-
Why Is Genetic Testing Important?
-
Early Detection: Helps identify conditions before birth.
-
Informed Choices: Parents can make well-prepared decisions regarding care, treatment, and next steps.
-
Better Pregnancy Management: Doctors can monitor pregnancies more closely if risks are identified.
-
Peace of Mind: For many parents, normal results bring reassurance during pregnancy.
Who Should Consider Genetic Testing?
While genetic testing is optional, it may be particularly recommended for:
-
Women aged 35 and older (higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities).
-
Couples with a family history of genetic disorders.
-
Pregnancies where ultrasound shows abnormalities.
-
Parents who are carriers of genetic conditions.
Risks and Considerations
-
Screening tests (like NIPT) pose no risk to the mother or baby.
-
Diagnostic tests (CVS, amniocentesis) carry a very small risk of miscarriage, so doctors carefully evaluate before recommending them.
-
Emotional impact: Results may cause stress, so counselling and medical guidance are essential.
Final Thoughts
Genetic testing in pregnancy is a powerful tool that supports parents with knowledge and reassurance. While not every pregnancy requires these tests, they can be life-changing for families at risk of genetic conditions. Always discuss your options with a qualified healthcare provider to choose what’s right for you and your baby.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0