Decoding the Drive: An Essential Guide to Car Key Programming

Car keys have evolved far beyond simple pieces of cut metal. Today, they are sophisticated electronic devices, complete with transponder chips and remote entry fobs, that communicate directly with your vehicle's immobilizer system. This advancement is a crucial security measure, but it also means that replacing or adding a new key is no longer a simple hardware store affair—it requires Car Key Programming. Understanding this process is key to saving time, money, and avoiding a security headache.
Why Programming is Necessary
The core reason for programming lies in modern automotive security. The small transponder chip embedded in the key (or key fob) contains a unique serial number and cryptographic key. When the key is inserted into the ignition (or simply present in the car for a "smart key" system), the vehicle's onboard computer, or Electronic Control Unit (ECU), sends a radio frequency signal to the chip. The chip must then send a correct, unique response. If the response is valid, the ECU allows the engine to start. If it's invalid—or if there's no chip at all—the car's immobilizer is activated, and the engine will not turn over, even if the key physically fits the lock.
Programming is the act of teaching the car's ECU to recognize and accept the unique code of a new key or fob, thereby adding it to the vehicle's list of authorized keys.
The Two Main Programming Methods
The complexity of the programming process largely depends on the make, model, and year of the car, and whether you are programming a transponder chip (to start the car) or just a keyless entry remote (to lock/unlock doors).
-
Onboard Programming (DIY): Many older or specific models (often some GM, Ford, and older Japanese cars) allow for what is called "onboard programming." This method is detailed in the vehicle's owner's manual and can be done by the owner, typically involving a sequence of actions like turning the ignition key on and off a specific number of times, holding buttons on the remote, or pressing a hidden button. This puts the car into a "learn mode," allowing it to accept the new key/fob's code. This is usually the cheapest and fastest option, provided you have at least one existing, working key.
-
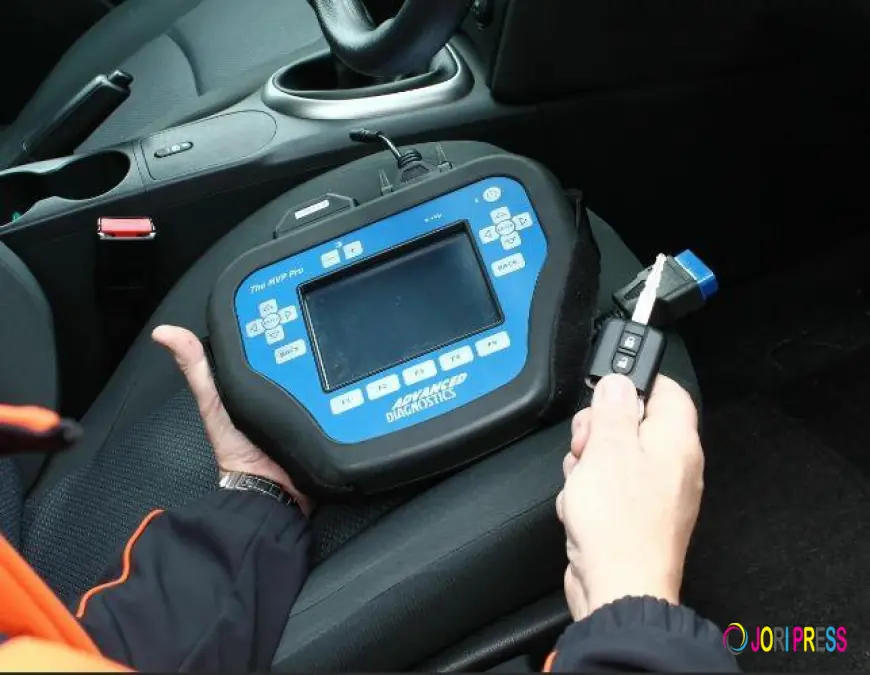
OBD-II Programming (Professional Required): For most modern vehicles and those that require a higher level of security access, programming must be done through the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) port. This requires specialized diagnostic equipment, often referred to as a "dealer tool" or an Auto Locksmith Programmer. The professional connects this device to the car's port and communicates directly with the ECU to input the new key's data. This method is essential when all original keys have been lost or when the vehicle's system is more complex, often involving a PIN code or security access from the manufacturer.
The Tools and The Professionals
While onboard programming requires little more than your existing key, the new key/fob, and your owner's manual, OBD-II programming necessitates professional-grade tools.
-
Auto Locksmiths: These specialists have invested in the programming equipment and are often the most affordable and convenient option, offering mobile services. They can program a wide range of car keys, including transponder keys, remote key fobs, and proximity smart keys.
-
Dealerships: They are guaranteed to have the correct, manufacturer-specific tools and software. While reliable, they are often the most expensive option and usually require you to tow the vehicle to their location if you have no working keys.
A Note on Key Quality
Before programming, ensure you have the correct key blank and the proper FCC ID/part number for your vehicle. A physically correct but electronically mismatched key may not program correctly, leading to partial function (e.g., the remote works, but the car won't start). Always source keys from a reputable supplier or professional to ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s system.
By understanding the difference between onboard and OBD-II programming, and knowing when to call a professional, you can confidently navigate the world of car key programming.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0