Navigating Skin Whitening Treatments
Navigating Skin Whitening Treatments
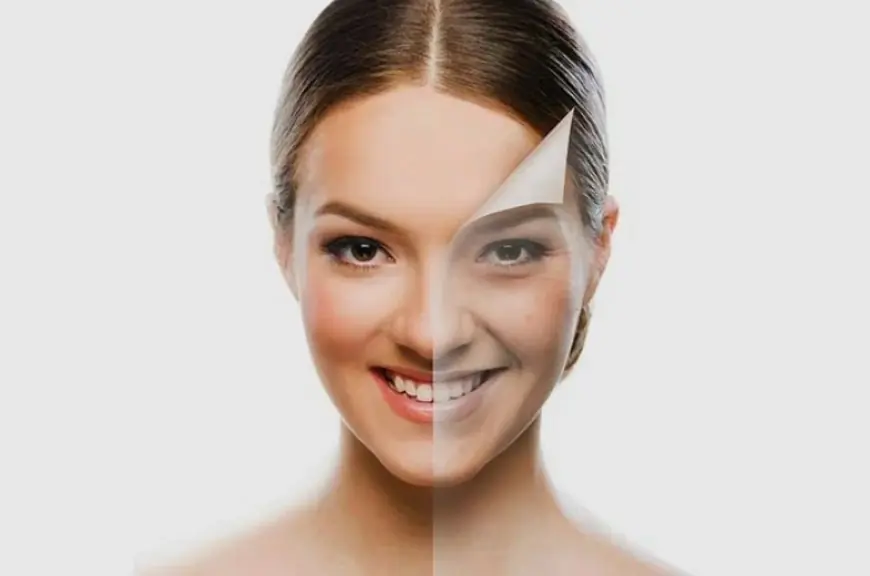

Navigating the complex world of skin whitening treatments can be a daunting and often risky endeavor. Driven by a global obsession with lighter complexions, an expansive market has emerged, offering everything from over-the-counter creams to professional medical procedures. While the desire for a brighter, more even skin tone is understandable, it is crucial to approach these treatments with caution, armed with knowledge about their ingredients, potential risks, and long-term effects. A well-informed consumer can make safer choices and avoid the significant health hazards associated with many of these products and procedures. Many clinics offer a range of treatments for skin whitening in Islamabad, from chemical peels and laser therapy to glutathione injections and IV drips.

The most accessible and widely used category of skin whitening products are topical creams, lotions, and serums. These products typically contain active ingredients designed to inhibit melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin color. Common ingredients include hydroquinone, arbutin, kojic acid, and vitamin C. Hydroquinone is one of the most effective and widely studied lightening agents, but its use is restricted in many countries due to concerns about its potential to cause ochronosis, a permanent skin discoloration, and its possible link to cancer. Products containing hydroquinone should only be used under medical supervision for a limited period. Arbutin, a derivative of hydroquinone, is considered a safer alternative, while kojic acid, derived from fungi, is another popular option. Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, can help brighten the skin and fade dark spots, but its effects are generally milder. When choosing a topical product, it is essential to read the ingredients list carefully and opt for products from reputable brands that comply with safety regulations.
Beyond topical applications, a variety of in-office procedures are available for those seeking more dramatic results. Chemical peels, for example, involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate the top layers, revealing a fresher, more even-toned layer underneath. The strength of the peel can vary, from mild glycolic acid peels to more aggressive trichloroacetic acid peels. While effective for treating hyperpigmentation and sun damage, chemical peels can cause redness, irritation, and even scarring if not performed by a trained professional. Similarly, laser treatments, such as fractional lasers or Q-switched lasers, can target and break down melanin in specific areas, effectively treating dark spots and uneven skin tone. These procedures require multiple sessions and can be expensive, and there is a risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones.
One of the most talked-about and controversial skin whitening treatments is glutathione, a powerful antioxidant naturally produced by the body. Glutathione injections are marketed as a way to whiten the entire body, with proponents claiming it works by deactivating the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. However, the use of glutathione for skin whitening is not approved by major health organizations, and its safety and efficacy for this purpose are not scientifically established. Receiving these injections from unlicensed practitioners or in unsterile environments can lead to serious health complications, including kidney damage, liver dysfunction, and infections. The lack of regulation surrounding these treatments makes them particularly dangerous.
Navigating these options requires a proactive and informed approach. The first and most crucial step is to consult a board-certified dermatologist. A dermatologist can accurately diagnose the cause of skin discoloration and recommend a safe and effective treatment plan tailored to an individual’s skin type and concerns. They can also prescribe safe concentrations of active ingredients and monitor for any adverse reactions. It is vital to be skeptical of products and treatments that promise instant or drastic results, as these are often unregulated and potentially harmful.
Furthermore, a comprehensive approach to skin health involves more than just treatments. Sun protection is paramount, as UV radiation is the primary driver of hyperpigmentation. Regular use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, along with protective clothing and hats, is non-negotiable for maintaining an even skin tone. A healthy diet, adequate hydration, and a consistent skincare routine can also contribute to a brighter complexion.
In conclusion, the journey to a lighter, more even skin tone is a personal one, but it should not come at the expense of one's health. By understanding the different types of treatments, recognizing the risks associated with certain ingredients and procedures, and seeking professional medical advice, individuals can navigate this complex landscape safely.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0